Radioactivity
190 likes | 309 Vues
This resource delves into the discovery and significance of nuclear radiation, including alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. Highlighting key historical figures such as Antoine Becquerel and Marie Curie, it explores the evolution of our understanding of radioactivity and its implications in science. The text discusses the mechanisms of alpha and beta decay, the role of neutrinos, and introduces various radioactive isotopes and their applications in fields like medicine and industry. Learn about the safety measures and advancements in the study of radioactivity.

Radioactivity
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Radioactivity Periodicity http://www.phy.bris.ac.uk/groups/particle/PUS/A-level/Standard_Model.htm
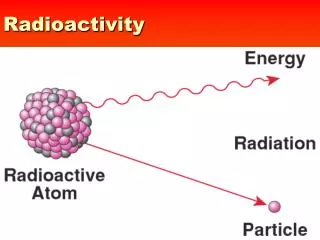
Nuclear RadiationIf there was any remaining doubt the discovery of nuclear radiation ended any consideration that atoms were indivisible. Not only could electrons be removed, the nucleus itself could fall apart! α Alpha radiation emitted from the nucleus β Beta radiation emitted from the nucleus, or γ Gamma radiation E = hν
Antoine Becquerel accidentally discovered Uranium salts because film placed next to the salts became exposed without benefit of light. • In 1898, Marie Curie discovered that pitchblend, a uranium ore, emits more radiation than uranium itself. She deduced that this ore contains, in very small quantities, one or more elements much more active that uranium. With the assistance of her husband Pierre Curie and after two years of effort, she arrived at isolating two new elements: Polonium (named thus in tribute to her homeland) and Radium. It was then that Marie Curie invented the word "radioactivity". http://molaire1.perso.sfr.fr/e_radioactiv.html National Council on Radiation Protection & Measurements (2009, March 5). Medical Radiation Exposure Of The U.S. Population Greatly Increased Since The Early 1980s. ScienceDaily. Retrieved November 23, 2012, from http://www.sciencedaily.com /releases/2009/03/090303125809.htm
In alpha decay the nucleus spontaneously splits into a daughter particle and a helium nucleus.
Examples of alpha decay To write the equation for alpha decay, use the following formula:
Quiz • What is an alpha particle? • How do you write the greek letter for an • alpha particle? • Write the balanced nuclear equation • for an isotope of 238U which undergoes alpha decay. • Is alpha decay a chemical reaction or a nuclear reaction? • A nuclear reaction. A helium nucleus: α (http://abyss.uoregon.edu/~js/ast123/lectures/lec07.html not in our text book)
Beta decay: In beta decay either an electron or a positron are expelled from the nucleus. A neutrino or antineutrino is also expelled.
Notice that in beta decay the number of protons increases. The electrons do not come from the electron cloud, which is why the neutrino or antineutrino is also expelled. (gamma radiation may also be expelled) Neutrinos have no charge and almost no mass and were predicted by Wolfgang Pauli to explain why beta decay didn’t violate the law of conservation of matter and energy. http://curriculum.cna.ca/curriculum/cna_radiation/beta_decay-eng.asp?bc=Beta%20Decay&pid=Beta%20Decay A cool animation of beta decay. http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/particles/neutrino.html
Radioactive isotopes which emit beta particles are called beta emitters. Below is list of some beta emitting radioactive isotopes. • Carbon-14is used in carbon dating artifacts and as a medical tracer • Cesium-137is used in brachytherapy to treat various types of cancer and to • measure the flow of oil in pipelines. • Cobalt-60 • Hydrogen-3 (tritium) • Iodine-129 • Iodine-131is used as a medical tracer • Nickel-63is used to detect explosives, and in voltage regulators and • current surge protectors in electronic devices. • Promethium-147is used in electric blanket thermostats, and to gauge • thickness of thin plastics, thin sheet metal, rubber, textile and paper. • Sodium-24is used to locate leaks in industrial pipelines, oil well studies • and in medical diagnostics. • Strontium-90is used as a power source for weather satellites and navigation buoys • Sulphur-35is used in manufacturing sensors and medical treatments. • Technetium-99mis used in nuclear medicine as a radioactive tracer • Thallium-204is used to measure the dust and pollutant levels on filter paper, • and in gauges used to measure the thickness of plastics, sheet metal, rubber, • textiles, and paper. http://curriculum.cna.ca/curriculum/cna_radiation/beta_emitters-eng.asp?bc=Common%20Beta%20Emitters&pid=Common%20Beta%20Emitters
Gamma radiation. http://faculty.virginia.edu/metals/cases/prescott2.html Interesting article about technetium.
Penetrating power of alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. http://www.frankswebspace.org.uk/ScienceAndMaths/physics/physicsGCE/D1-3.htm http://sciencecity.oupchina.com.hk/npaw/student/glossary/ionizing_power.htm http://library.thinkquest.org/C006669/data/Chem/atomic/development.html
Review • Which type of radiation has no charge, and is high energy? • Which type of radiation is the size of an electron, is either positive or negative? • Which type of radiation is basically a helium nucleus? • Which two types of radiation normally occur together? gamma beta alpha Beta and gamma, also neutrinos
Half- life • Radioactivity is spontaneous. It occurs regardless of the temperature, surface area, or any of the usual things which make chemical reactions occur. The rate depends only on the amount of “parent nuclide” present. • We report the rate as a “half life” The half life depends upon the stability of the nucleus. The more stable the nucleus, the longer the half life. At the end of the period of time called “half life” there is half as much of the “parent isotope” as at the beginning. ½ → ¼ → 1/8 → 1/16 → 1/37 0.5 → 0.25 → 0.13 → 0.06→ 0.03 T → 2T → 3T → 4T → 5T
Half life equations • AE is the amount of substance left • A0 is the original amount of substance • t is the elasped time • t1/2 is the half-life of the substance Other variations on the half-life equation are as follows: An example problem is if you originally had 157 grams of carbon-14 and the half-life of carbon-14 is 5730 years, how much would there be after 2000 years? There would be 123 grams left. http://library.thinkquest.org/10429/low/nuclear/nuclear.htm
How can we predict which atoms will decay and what type of decay they will experience? • Alpha decay reduces the atomic number by two protons and two neutrons. • So much energy is released that gamma radiation is frequently given off as well. http://mail.rdcrd.ab.ca/~smolesky/physics30/5Matter/day_8%20objective.htm http://chemed.chem.wisc.edu/chempaths/GenChem-Textbook/Nuclear-Chemistry/chemprime/CoreChem3ANuclear_Stability-745.html
http://mail.rdcrd.ab.ca/~smolesky/physics30/5Matter/day_8%20objective.htmhttp://mail.rdcrd.ab.ca/~smolesky/physics30/5Matter/day_8%20objective.htm How can we predict which atoms will decay and what type of decay they will experience? Beta decay will increase the atomic number so the daughter nuclide will be more stable than the parent. http://chemed.chem.wisc.edu/chempaths/GenChem-Textbook/Nuclear-Chemistry/chemprime/CoreChem3ANuclear_Stability-745.html
Small atoms with too many protons will undergo electron capture or positron emission to obtain stable nucleii http://mail.rdcrd.ab.ca/~smolesky/physics30/5Matter/MatterPics/formulas/positron.gif
Gamma radiation is thought to be a release of nuclear energy. No apparent change to the number of protons or neutrons is necessary for gamma radiation. For the original images and explanations… http://mail.rdcrd.ab.ca/~smolesky/physics30/5Matter/MatterPics/radioactive%20decay/AlphaBetaGamma2.jpg
More practice Label where alpha and beta decay are most likely.