What is Cancer?
400 likes | 2.55k Vues
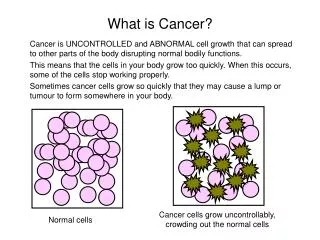
What is Cancer?. Definition: A disease caused by an uncontrolled division of abnormal cells in a part of the body It then spreads to other parts of the body through the blood and lymph systems. Cancer is not just one disease but many diseases. How Does Cancer Kill YOU ?. Origins of Cancer.

What is Cancer?
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What is Cancer? • Definition: • A disease caused by an uncontrolled division of abnormal cells in a part of the body • It then spreads to other parts of the body through the blood and lymph systems. • Cancer is not just one disease but many diseases. • How Does Cancer Kill YOU?
Origins of Cancer • All cancers begin in cells, the body’s basic unit of life. • When do normal cells become cancer cells:
How does chemotherapy work? • Where did Chemotherapy come from? • Chemotherapy drugs attack reproducing cells, they cannot tell the difference between reproducing cells of normal tissue and cancer cells. • The damage to normal cells can cause side effects • Each time chemo therapy is given, it involves trying to find a balance between killing the cancer cells and saving the healthy cells.
Definitions • Free Radical: • Atoms or groups of atoms with an odd (unpaired) number of electrons and can be formed when oxygen interacts with certain molecules. Antioxidants: • A molecule capable of inhibiting the oxidation of other molecules.
Essential Oils do not prevent, treat, or cure disease. Your lifestyle choices can help prevent disease. Your doctor treats symptoms and fixes broken parts. Your body cures disease!
How long have EO’s Been Around? • Essential oils were mankind’s first medicine • Over 500 references in the Bible to EO’s • The Three wise men brought Frankincense & myrrh to baby Jesus • Egypt • Used in the embalming process • Temples were dedicated to the production and blending of oils & recipes were found on the walls
What are Essential Oils? • The volatile liquids that are distilled from plants (including their respective parts such as seeds, bark, leaves etc.) • Purity & therapeutic value is determine partly by the chemical constituents or the oil’s chemistry. • Some of the variables that effect this are: • Altitude, climate, soil condition, geographical region, harvest season & methods, distillation process etc.
Producing a Pure Therapeutic Grade Essential Oil. • High Temp and pressure, rapid processing & the use of chemical solvents often are used during the distillation process to get more oil at a faster rate. • These oils may smell just as good & cost much less, but will lack most, if not all, of the chemical constituents necessary to produce the expected therapeutic benefits. • Producing pure oils can be costly due to the amount of plant material required to extract 1 pound of pure EO. • 1lb pure Melissa oil sells for $9,000-$15,000 but requires 3 tons of plant material to produce.
Benefits of Pure Therapeutic- Grade of EO’s • Regenerating, oxygenating, & immune defense properties of plants. • Some constituents are so small in molecular size that they can quickly penetrate the tissues of the skin. • Lipid soluble & are capable of penetrating cell walls , even if they have hardened because of an oxygen deficiency. Takes about 20 min to penetrate every cell in the body & are then metabolized like nutrients. • EO’s contain oxygen molecules which help to transport nutrients to starving human cells. This also helps to boost the immune system. • Powerful antioxidants that create an unfriendly environment for free radicals. • EO’s have been shown to destroy tested bacteria and viruses while simultaneously restoring balance to the body.
Ways to Use EO’S • Aromatically: • Limbic system/olfactory nerves: directly connected to the parts of the brain that control: heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, memory, stress and other emotions. • Diffused oils don’t mask odors; they alter the structure of the molecules that create odors. • Research also shows that cold-air diffusing may: • Reduce bacteria, fungus, mold and unpleasant odors. • Relax the mind and body and relieve tension • Improve concentration, alertness and mental clarity.
Ways to Use EO’S • Internally: • Consuming the essential oil into the body. • FDA has approved some essential oils for internal use and given them the designation of GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe for human consumption) • ONLY Pure therapeutic grade essential oils should be used for internal consumption. • Topically: • Process of applying directly on the body or area of concern. 1-3 drops are adequate for an adult. • On the bottoms of the feet, behind the ears and inside of the wrist are where the oils are absorbed the quickest. • Some oils need to be diluted with a carrier oil due to their potency & may irritate the skin.
Frankincense • The King of Oils • Calming, Revitalizing and Uplifting. • Cytophylic (Stimulates the regeneration of cells), immune boosting toni and anti-carcinogistic • Has been documented all over the world to have a very strong cancer deterrent factor. One of its gifts is its chemistry which allows it to cross the blood brain barrier and facilitates oxygenation of cells for optimal communication at the cellular level.
Peppermint • One of the oldest and most highly regarded herbs for soothing digestion and calm nausea. • Has the ability to decrease anxiety and provide relief along most pain sensors in the body. • The cooling effect of peppermint releases stress and tension in the body. • Comprises of Vitamins A & C which are big antioxidants
Lavender • Swiss army knife of Oils • It has sedative action on the heart and calms the cerebro-spinal excitability. • Helps with cuts, bruises, burns etc. • Revs up the immune system while conveniently fighting infection at the same time. • Enhances immunity by increasing the production of white blood cells
Mother nature has passed the test of time—live life to it’s fullest.”