Understanding Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection, and Thermal Resistance Mechanisms
230 likes | 402 Vues
Heat can be transferred through conduction, convection, and radiation, with conduction occurring via direct thermal contact. The ability of materials to conduct heat is indicated by thermal conductivity values (measured in W/m-K), with metals like copper and aluminum being excellent conductors. Conversely, materials such as wood and Styrofoam are effective insulators. The rate of heat transfer also depends on the temperature gradient and surface area in contact. For layered materials, thermal resistance describes the performance in maintaining temperature, affecting energy efficiency.

Understanding Heat Transfer: Conduction, Convection, and Thermal Resistance Mechanisms
E N D
Presentation Transcript
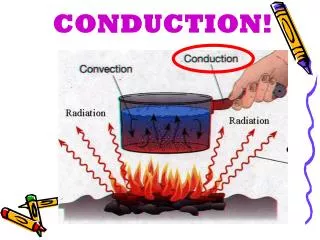
Conduction Energy flow from direct thermal contact Radiation Energy radiating from an object into surroundings Transfer Mechanisms • Heat can be transferred in three ways. • Transfer can include more than one way. • Convection • Fluid flow carrying energy
Direct Contact • Items in direct contact transfer heat. • Molecules in hot regions have greater kinetic energy. • Elastic collisions with cool molecules • Kinetic energy transfer at boundary
Heat flow within an object is due to transfer by conduction. Thermal conductivity (k) measures the ability for heat to move in a material. Measured in W / m-K High number means high rate of transfer Material Thermal Cond. Air 0.026 W/m-K Stryrofoam 0.029 W/m-K Wood 0.11 W/m-K Water 0.61 W/m-K Glass 0.8 W/m-K Concrete 1.0 W/m-K Steel 46 W/m-K Aluminum 240 W/m-K Copper 400 W/m-K Thermal Conductivity
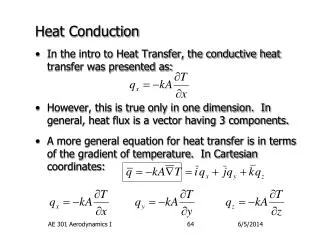
Heat Flow Rate • The rate of heat flow depends on the temperature gradient. • Change in temperature with distance • Depends on surface area A for contact. A H T + DT T Dx
Conductors and Insulators • Thermal conductors have high values of k. • Metals with conducting electrons • Greater than 10 W/m-K • Still air is an excellent thermal insulator. • Materials that trap air are good: wood, styrofoam • Vacuum would be the best.
A lake with a flat bottom and steep sides has a surface area 1.5 km2 and is 8.0 m deep. The surface is at 30 C and the bottom is at 4 C. What is the rate of heat conduction through the lake? Convert area to m2. 1.5 km2 = 1.5 x 106 m2 Use the equation for heat flow. H = -kA(DT/Dx) -(0.61 W/m-K)(1.5 x 106 m2) (26 K) / (8.0 m) H = -3.0 x 106 W. Swimming Hole
Two Layers • If there are two layers in thermal contact, the rate of heat flow must be the same for both. • Energy doesn’t accumulate in the layer. T3 T2 T1 H H Dx2 Dx1
Thermal Resistance • For an arbitrary set of layers the intermediate temperature is unknown. • Define thermal resistance • For multiple layers R adds T3 T2 T1 H H R2 R1
In the US, thermal resistance is measured per unit area. R = Dx / k Units are ft2F hr / BTU 1 BTU = 1055 J Material R-factor Glass (1/8”) 1 Brick (3½”) 0.6 – 1 Plywood (1/2”) 0.6 Fiberglass insulation (1”) 4 R-Factor