5-2 Notes: Sumer
70 likes | 273 Vues
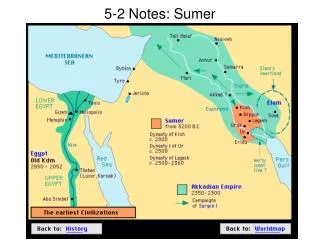
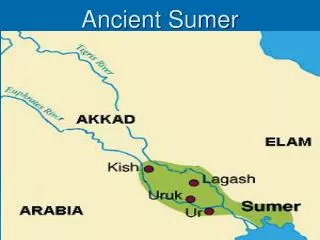
5-2 Notes: Sumer. Ancient Sumer. (3000 B.C.E.) Large surpluses of crops in southern Mesopotamia allowed large amounts of skilled workers to live in cities of southern Mesopotamia

5-2 Notes: Sumer
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Ancient Sumer • (3000 B.C.E.) Large surpluses of crops in southern Mesopotamia allowed large amounts of skilled workers to live in cities of southern Mesopotamia • Although fighting took place between rival cities, they shared a common religion, agricultural system, and some of the world’s earliest advancements such as the wheel, sailboats, and writing
Cuneiform • Sumer is credited with inventing cuneiform, the world’s first writing system • System used at first to record farm surpluses with sharp reeds into soft clay tablets • Earliest tablets (3500 B.C.E.) featured symbols that looked like what they described; gradually these symbols became simpler, forming a language of over 500 signs • Cuneiform was difficult to read and write, so schools were set up to teach it • After years of studying, graduates became scribes (writers) whose job was to record information (letters, stories, laws, songs
City-States • Life in Sumer was dominated by city-states, or self-governing cities that also controlled surrounding villages • Rival city-states often went to war with each other over resources (normally control of water) • Cities were walled; gates were important access points and markets in the city • Palace was the center of city life; Kings served as generals, judges, engineers
Religion in Ancient Sumer • In the center of Sumerian cities stood the ziggurat, a large mud-brick building with a temple on top • Ziggurats employed thousands of people as weavers, barbers, musicians, craft-workers, bakers, scribes and more • Sumerian religion was polytheistic, meaning that they worshipped many gods that represented love, war, water, and other things • Sumerians believed that gods were responsible for the well being of their families and cities
Sargon of Akkad • Sargon, from the city-state Kish, united the city-states of Sumer under one government around 2300 B.C.E. • Sargon founded a new city, Akkad, to be the capital of what is considered to be the world’s first empire • Sargon expanded north and west into Mesopotamia until his kingdom stretched over 900 miles • Sargon used cuneiform to communicate and unite his empire