AC Circuits
220 likes | 456 Vues
AC Circuits. Physics 102 Professor Lee Carkner Lecture 23. PAL #23 Alternating Current. 240 W lightbulb, V rms = 120 V, 60 Hz the rms current V rms = I rms R, I rms = V rms /R = 120/240 = 0.5A the maximum current I max = (2) ½ I rms = (2) ½ (0.5) = 0.707 A the maximum power

AC Circuits
E N D
Presentation Transcript
AC Circuits Physics 102 Professor Lee Carkner Lecture 23
PAL #23 Alternating Current • 240 W lightbulb, Vrms = 120 V, 60 Hz • the rms current • Vrms = IrmsR, Irms = Vrms/R = 120/240 = 0.5A • the maximum current • Imax = (2)½Irms = (2)½(0.5) = 0.707 A • the maximum power • Pmax = I2maxR = (0.707)2(240) = 120 W • the average power • Pav = I2rmsR =(0.5)2(240) = 60 W • the power at time equals 1/120 second • I = Imax sinwt = Imax sin(2pft) = Imax sin [(2)(p)(60)(120)-1] = Imax sin (p) = 0 • P = 0 • Completed 1/2 cycle, I back to zero
AC Circuit Elements • In an AC circuit we get resistance-like effects from three different elements: • Capacitors (Reactance, XC) • We can combine them together to get the impedance (Z) • We can then use Ohm’s Law to find the current • For AC circuits we also define 3 different values of V and I • The instantaneous (I = Imax sinwt) • The rms (Irms = 0.707 Imax)
AC and Capacitors • The ”resistance” of a capacitor is the reactance, XC XC = 1/(wC) • High frequency and large capacitance means less reactance • The voltage and the current across the capacitor are not in phase • Shift the current sine wave ¼ cycle “backwards” from the in-phase situation
Inductive Reactance • We can define the way in which an inductor impedes the current with the inductive reactance: XL = wL • Creating a rapidly changing magnetic field and thus a strong back emf DVL = IXL
Inductors and Phase • What is the phase shift between V and I? • look at the slope of the current sine wave • The induced voltage is zero when the current is a maximum (since that is where the current is not changing) • The voltage leads the current by 90 degrees (V is max 1/4 cycle before I)
Reactance and Frequency • Resistor • Capacitor • Inductor • Low current at high frequency
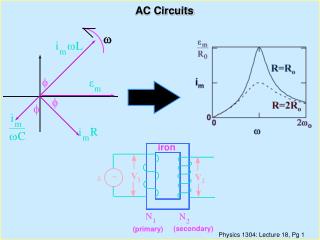
RCL and AC • Let’s combine all three elements together • If you combine a resistor, capacitor and an inductor into one series circuit, they all will have the same current but all will have difference voltages at any one time • Voltages are all out of phase with each other
RLC Impedance • Called the impedance (Z) Z = (R2 + (XL - XC)2)½ • The voltages for the inductor and capacitor are 180 degrees opposed and so subtract • The total voltage is: • Can think of Z as a generalized resistance for any AC circuit
Phase Angle and Power Factor • They are separated by a phase anglef, defined as: cos f = IR/IZ = R/Z • We know that power can be written P = IV • Can write power as: Pav = IrmsVrms cos f • Note that only the resistor dissipates power
Next Time • Read 22.1-22.4, 22.7 • Homework Ch 21, P 64, 65, Ch 22, P: 3, 7
Consider a sinusoidally varying current with a maximum value of 1 A. What is the value of the current at ¼, ½ and ¾ of the cycle? • ¼, ½, ¾ • 0, -1, 1 • 1, 0, -1 • 0, 1, 0 • 1, 1, 1
Consider a sinusoidally varying current with a maximum value of 1 A and an angular frequency of p. What is the value of the current at time equals ½ second and one second? • ½, 1 • 1, 2 • 0, 1 • 1, 0 • 0, 0
Consider two sine waves with a phase shift of p radians. When one wave is at its maximum value, the other is at, • its minimum value • 0 • its maximum value • √2 times its maximum value • p times its maximum value