Break Even Analysis
120 likes | 294 Vues
Break Even Analysis. [ Chapter 9 ]. Objectives. Upon completion of this chapter students will be able to: Identify different type of costs. Define type of costs. Contribution Contribution and Variable Rate Understand break-even point Able to solve the chapter’s problems. Type of Costs.

Break Even Analysis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Break Even Analysis [Chapter 9]
Objectives • Upon completion of this chapter students will be able to: • Identify different type of costs. • Define type of costs. • Contribution • Contribution and Variable Rate • Understand break-even point • Able to solve the chapter’s problems.
Type of Costs Two type of costs are incurred to run a business: • Fixed Cost – are those costs that has no relation with the sales volume. Examples: • Depreciation costs, Interest expense, Property taxes, and others. • Variable Cost – are cost that has linear relation with sales volume. Examples: • Food Costs, Beverage costs, Salaries and so on.
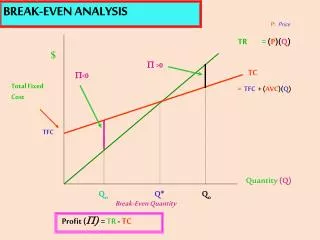
Contribution • Contribution or Gross Profit : • Revenue – Variable Cost = Contribution • Net Profit = • Contribution (Gross Profit) - Fixed Cost
Profit & Loss Statement Revenue (Sales) Less : Variable Cost Contribution (Gross Profit) Less: Fixed Cost Net Profit Example: Sales of a Company is $100,000 Variable Cost is $70,000 Fixed Cost is $20,000 Find Gross Profit and Net Profit?
Solution Sales $100,000 Variable Cost $70,000 Contribution(GP) $30,000 Fixed Cost $20,000 Net Profit $10,000
Contribution and Variable Rate ( %) Contribution Contribution Rate = ___________ X 100 Sales Variable Cost Variable Rate = ______________ X 100 Sales
Example • Sales $100,000 • Variable Cost $70,000 • Contribution(GP) $30,000 • Fixed Cost $20,000 • Net Profit $10,000 • Variable Rate = 70,000 X 100 = 70% 100,000 Contribution Rate = 30 %
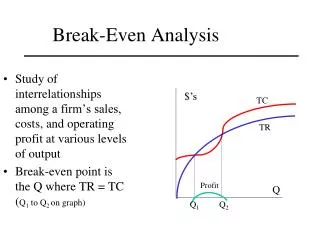
Conclusions • Variable % + Contribution % = 100% • Variable Rate + Contribution Rate =1 • Contribution Rate = 1 – Variable Rate • Total Cost = Variable Cost + Fixed Cost • Total Sales = Total Cost Called BEP • BEP - Break Even Point
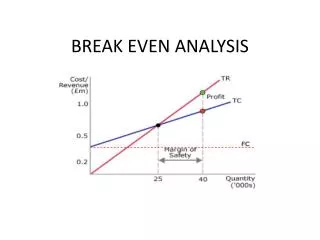
Break –Even - Analysis • Purpose • To establish the sales level required to cover all costs. • Required Tools • We need to have Fixed Costs • We need to have Contribution Rate or % • BEP = Fixed Costs (FC) • Contribution Rate (CR)
Fixed Cost=$5,400Variable Costs=$15,000Sales = $20,000 Find Sales to break – even? • Step 1) Find Variable Cost % (Rate) • VR = VC/ Sales = .75 or 75% • Step 2 ) Find Contribution Rate CR = 1- 0.75 = 0.25 • Step 3) BEP Sales = FC / CR • BEP Sales = 5,400 / 0.25 = 21,600