Cell Structure Unveiled: History, Theory, and Function
110 likes | 205 Vues
Explore the fascinating journey of cell discovery from Hooke to modern technologies, understanding the essence of cell theory, and the distinctions between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Learn about DNA, organelles, and cell movement. Discover the significance of cells in living organisms.

Cell Structure Unveiled: History, Theory, and Function
E N D
Presentation Transcript
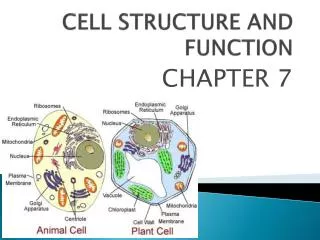
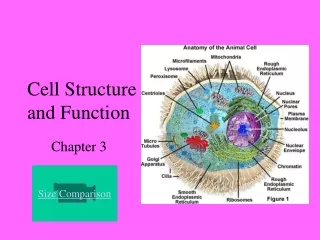
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CHAPTER 7
Section 1 NOTES • The CELL is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. • CELL THEORY states • 1. All living things are composed of cells • 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things • 3. New cells are produced from living cells
The History of the Cell • 1. Robert Hooke – viewed a thin slice of cork with an early compound microscope (1665) • Name them cells because of a monastery’s tiny rooms. 2. Anton van Leeuwenhoek - observed tiny organisms in drops of pond water (1674)
History of the Cell • 3. Matthias Schleiden – Concludes that all plants are made of cells (1838) • 4. Theodor Schwann – Based upon Schleiden’s work, concludes animals are living so all animals are also made up of cells (1839
History of the Cell • 5. Rudolph Virchow – proposes that all cells come from existing cells completing the cell theory (1855) • 6. Lynn Margulis • Endosymbiont Theory – Prokaryotic organisms (mitochondria and chloroplasts) were once free living but began a symbiotic relationship with larger multi-cellular organisms. • Contain their own DNA • Have their own membranes • Reproduce independent of cell
Endosymbiotic Theory • Contain their own DNA • Have their own membranes • Reproduce independent of cell
Studying the Structure and Movement of the Cell • What is a Light microscope? • Advantages/Disadvantages? • What is an Electron microscope? • Advantages/Disadvantages? *** NEW TECHNOLOGY 1990s *** Scanning probe microscope – traces the surface of a sample. • Images of DNA, Protein molecules, and other important biological structures
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes • Complete the Venn Diagram to compare the characteristics of a prokaryote and a eukaryote.
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes • Both are living things • Both are surrounded by a cell membrane • Both contain DNA What class of organic molecules is DNA? What is its monomer? 3 Parts? What is the function of DNA?
Prokaryotes • 1. Do not contain a nucleus • 2. Smaller and simpler • 3. DNA is free floating within the cell • 4. Grow, reproduce, respond to environment Some can move or swim • Example: bacteria
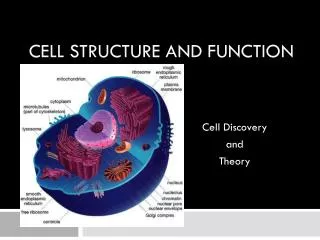
Eukaryotes • 1. Contain a nucleus that contains DNA separate from rest of cell • 2. Larger and more complex • 3. Dozens of Highly specialized membranes and structures • 4. Single celled to large complex multi-cellular organisms Examples: Plants, animals, fungi, and algae