SENTENCE PATTERNS
190 likes | 707 Vues
SENTENCE PATTERNS. Paragraph. 1 A genome is all the genetic material in the chromosomes of an organism. 2 The

SENTENCE PATTERNS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Paragraph 1A genome is all the genetic material in the chromosomes of an organism. 2The human genome includes about three billion base pairs that make up human DNA. 3The Human Genome Project, completed in 2003, was a 13-year, international effort to identify the 20,000-25,000 human genes and make them accessible for further biological study.4This research has catalyzed biotechnology.
Sentence Parts Subject – verb – direct object or subject complement -- modifiers 1 A genome is all the genetic material in the chromosomes of an organism. 2 The human genomeincludes about three billion base pairs that make up human DNA. 3 The Human Genome Project, completed in 2003, was a 13-year, international effort to identify the 20,000-25,000 human genes and make them accessible for further biological study. 4 This researchhas catalyzed biotechnology.
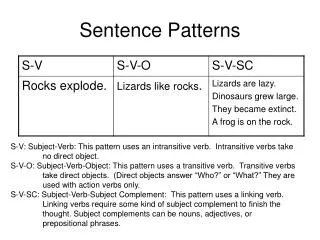
Sentence Patterns • The Dow Jones Industrial Average fell by 53 points. S-V • I will lie down. S-V-AC • A virusis a pathogen. S-V-SCN • All membersarepresent. S-V-SCA • The studentsworked the algebra problems. S-V-DO • Jane’s bossofferedher a raise. S-V-IO-DO • Didyouput the cake in the oven? S-V-DO-AC • Iconsideryou my best friend. S-V-DO-DOCA • The womenfound the candidate’s languageoffensive. S-V-DO-DOCA
1. S + V-int • The intransitive action verb takes no direct object. • Even if the action verb is followed by a prepositional phrase, the verb is still intransitive as long as it does not take a direct object. • Ex:The children are sleeping. Who is calling?
2. S + LV-be + ADV(Time/Place) One kind of intransitive verb is the linking verb of being. An LVmay be followed by an adverb indicating where or when. • The adverbial indicating where or when may be a prepositional phrase. Note: Subjects are indicated in the diagrams as NP1 for the first noun phrase in the sentence.
3. S + LV + SCA The verb of being is followed by an adjective that functions as the subjective complement. The subjective complement adjective may be a prepositional phrase.
4. S + LV + SCN The linking verb is followed by a noun that functions as the subjective complement. Note: The second noun, the subjective complement, is the same as the subject (Mr. James = teacher).
Grandma’s house always smelled like moth balls. NP1 LV ADJ subject subjective complement The air feels wintry today. NP1 LV ADJ subject subjective complement More Linking Verbs • The linking verb may be a word similar to “be,” such as “seem,” “appear,” “become,” or “looks.” • Or, it may be a verb relating to the senses.
My brother is taking his wife on a cruise. 5. S + V + DO The transitive action verb is followed by a direct object. Note: The second NP, the direct object, receives a different numerical designation (NP2) because it is not the same as the subject (NP1).
7. S + V + IO + DO The action verb is followed by an indirect object and then a direct object. Note: The indirect object and the direct object each receive a new numerical designation because each is different from the other and both are different from the subject.
Put the dog outside. V DO adverb complement 6. S + V + DO + Adv Comp The action verb is followed by a direct object, and the adverb complement completes the verb.
8. S + V + DO + DOCA The action verb is followed by a direct object. The direct object is followed by an adjective functioning as an objective complement. Note: The second NP, the direct object, receives a different numerical designation (NP2) because it is not the same as the subject (NP1).
9. S + V + DO + DOCN The action verb is followed by a direct object. The direct object is followed by a noun functioning as an objective complement. Note: The second NP, the direct object, receives a different numerical designation (NP2) because it is not the same as the subject (NP1). The third NP, the objective complement, receives the same numerical designation as the direct object (NP2) because it is the same as the direct object (Jacobsen = friend).