Reinforcement
120 likes | 445 Vues
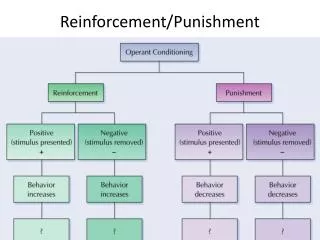
Reinforcement. Always functions to increase behavior. There must be a functional relationship between the behavior and the consequence (reinforcement). A maintenance or increase of the desired behavior must be observed in the future.

Reinforcement
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Reinforcement Always functions to increase behavior. There must be a functional relationship between the behavior and the consequence (reinforcement). A maintenance or increase of the desired behavior must be observed in the future. Positive reinforcement: + + The contingent presentation of or the offering of something perceived as positive, desired, or valued used to increase a desired behavior. Negative reinforcement: - - The contingent withdraw of or the taking away of something perceived as negative or undesirable used to increase a desired behavior.
Rules to think about when using reinforcment • Make the reinforcer contingent: The student must ONLY get the reinforcer after performing the target behavior. IF…then…. • Makes the behavior and the consequence explicit • Make the reinforcer immediate: The student must make the connection between “doing the behavior” and the reward. Immediate reinforcement also avoids the hazard of inadvertently reinforcing an intervening behavior. • Make the reinforcer meaningful: Different strokes for different folks…one person pleasure is another’s poison.
Types of reinforcers Social: Smiling, a handshake, nodding yes, clapping, a pat on the back, thumbs up, “nice job”, “Way to go”, “Yeah team”, “Group 1 has finished, have you?” Tangible: Stickers, a note home, blue ribbons, Black belt Physical Activity: Extra minutes swimming, playing favorite game, extra minutes playing not practicing Privileges: Squad leader, captain, collecting equipment, help teacher during study hall
Schedules of Reinforcement Different schedules of reinforcement affect a student’s behavior Continuous reinforcement: EVERY occurrence of the desired behavior is reinforced. Good luck! This type of reinforcement makes the student fairly dependent or satiated on the reinforcer. Use in developing a new behavior (shaping) or where the occurrence is initially low. A shift must be made to a more natural reinforcement schedule as soon as possible or extinction will occurr.
Intermittent Schedules of Reinforcement Two types: Ratio or interval schedules and fixed and variable Ratio schedules of reinforcement are determined by the NUMBER (ratio) of times the behavior occurs. FIXED RATIO: After you complete three hundred yards of warm-up….. After you complete 8/10 free throws…. After you read four pages in your book
VARIABLE RATIO In a variable ratio schedule, the student is reinforcer at an unpredictable rate. One time (series) it will be 5 or 8 or 3 or 10. The unpredictability of the reinforcement keeps the students behavior “high” and constant, because they have no idea when the next reinforcer will come.
Interval schedules of reinforcement are based on time. One occurrence of the behavior must be exhibited during a specified period of time. FIXED INTERVAL: After every five minutes if……. VARIABLE INTERVAL: Similar to the variable ratio schedule in that it is unpredictable to know when the reinforcer comes.
One variation is a limited-hold contingency: A LH restricts the time that is available to receive the reinforcer after the interval has been achieved: After 5 minutes of running, you have 2 minutes to get a drink. There is a time when the reinforcer is available and when it is not. All schedules of reinforcement are purposeful and temporary. More natural reinforcers and schedules help students to maintain behavior.