Classification of Matter-
360 likes | 398 Vues
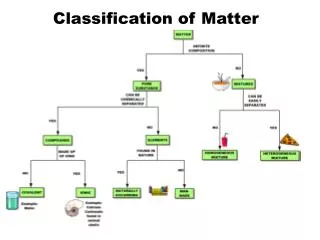
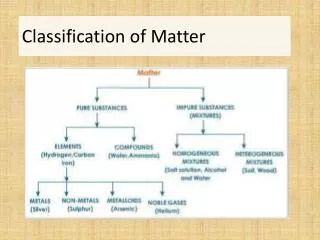
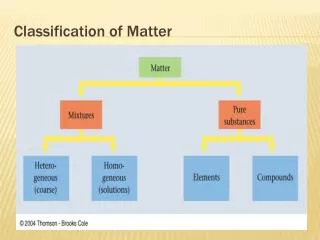
Classification of Matter-. Today’s Words Matter Solid Liquid Gas Surface tension Viscosity. Today’s Special Words Crystalline solids Amorphous solids Compressibility. Classification of Matter. Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space.

Classification of Matter-
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Classification of Matter- • Today’s Words • Matter • Solid • Liquid • Gas • Surface tension • Viscosity • Today’s Special Words • Crystalline solids • Amorphous solids • Compressibility
Classification of Matter Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. We can classify matter based on whether it’s solid, liquid, or gas. 2
Classifying Matterby Physical State Matter can be classified as solid, liquid, or gas based on the characteristics it exhibits. • fixed = keeps shape when placed in a container • indefinite = takes the shape of the container 3
Solids • Have definite shape and definite volume • Particles are tightly packed • though they may vibrate • The close packing of the particles results in solids being incompressible. • Solid particles vibrating • What is water? Solids vs liquids 4
Crystalline Solids • Some solids have their particles arranged in an orderly geometric pattern─we call these crystalline solids. • salt • diamonds • sugar 5
Amorphous Solids • Some solids have their particles randomly distributed without any long-range pattern─we call these amorphous solids. • plastic • glass • charcoal 6
Liquids • Do not have definite shape but do have definite volume • Particles are loosely packed • The close packing results in liquids being incompressible. 7
Liquids Viscosity Surface Tension Seen with water Molecules are attracted to each other Example: Water drops on grass Bug walking across pond Over filling a glass • Flows slower than water • Slows down a temperature goes down • Examples: • Cooking Oil • Car Oil • Syrup • Lava
States of Matter • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nrUBPO6zZ40&list=PLED25F943F8D6081C • http://labs.minutelabs.io/Brownian-Motion/ • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-QhU8eMR4IQ
Gases • In the gas state, the particles have complete freedom from each other. • The particles are constantly flying around, bumping into each other and the container. • In the gas state, there is a lot of empty space between the particles. • on average 10
Gases Because there is a lot of empty space, the particles can be squeezed closer together; therefore, gases are compressible. Because the particles are not held in close contact and are moving freely, gases expand to fill and take the shape of their container, and will flow. 11
Vapor 1 • Matter that exists in the gas state but is generally a liquid or solid at room temperature is called vapor. • Water, for example, is a liquid at room temperature. Thus, water vapor is the term for the gas state of water.
Particles slide past each other Definite Volume Definite Shape Particles close together Atoms Matter No definite shape Particles move quickly No definite volume
Thermal Energy Lecture 3.2a
Heat and Thermal Energy • Thermal Energy is the energy that moves in heat transfer Higher temp = higher thermal energy Lower temp = lower thermal energy
Temperature • Temperature: • A measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in an object
What Changes Thermal Energy? • 1. Temperature • 2. Amount of substance • More moving particles = more thermal energy
What Is Heat? High Temperature Objects • The transfer of energy between objects at different temperatures Energy ** Energy moves from high-temp. to low-temp. Low Temperature Objects
Thermal Energy is Related To…? • Kinetic Energy of molecules!! The more movement (Kinetic Energy) the molecules have, the more Thermal Energy an object has!!
Reaching The Same Temperature • The point at which both objects in contact reach the same temperature… Thermal Equilibrium ** NO CHANGE IN THERMAL ENERGY OCCURS!!
Changes of State Section 2b
Changes of State • There are six major changes of state • Freezing • Melting • Vaporization • Evaporation • Condensation • Sublimation
Freezing • Freezing – The change of state from a liquid to a solid. • As liquids cool their particles begin to slow, bringing them closer together • The freezing point of water is 0oC • Freezing is a loss of thermal energy
Melting • Melting – The change of state from a solid to a liquid. • As a substance absorbs heat energy the objects particles begin to heat up and move faster and farther away from one another. • The melting point of water is 0oC • Melting is a gain of thermal energy.
Vaporization • Vaporization – Process that occurs when a liquid becomes a gas known as boiling • Dependent on how strongly the particles in the object are held together. • The boiling point of water is 100oC • Vaoprization is a gain of thermal energy.
Evaporation • Evaporation – Occurs when a liquid acquires enough energy to become a gas only on the surface of a liquid. • Evaporation is a gain of thermal energy.
Condensation • Condensation – Occurs when a gas loses enough thermal energy to become a liquid. • Particles in a gas lose energy and begin to move slower, coming closer together. • Condensation is a loss of thermal energy.
Sublimation • Sublimation – Occurs when the surface particles of a solid gain enough energy to become a gas. • The object goes directly from a solid to a gas skipping the liquid phase. Ex. Dry Ice • Sublimation is a gain of thermal energy.
Definite Volume Particles slide past each other Definite Shape Melting/ Freezing Particles close together Atoms Matter Vaporization Evaporation Sublimation Condensation No definite shape Particles move quickly No definite volume
Phase Change • What happens when things melt, boil, etc.? • During a phase change, Thermal energy is either absorbed or released. • Solid to a Liquid and a Liquid to a Gas both Absorb Thermal Energy. • Gas to a Liquid and Liquid to a Solid both Release Thermal Energy.
Phase Change • What happens to substances when they are heated or cooled? • When objects are heated they Expand. • When objects are cooled the Contract. • Water is the only exception. It actually expands as it cools.
Phase Change • Change of State Graph