FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
230 likes | 571 Vues
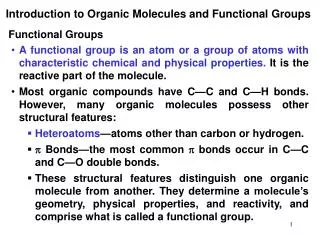
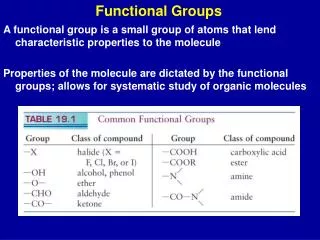
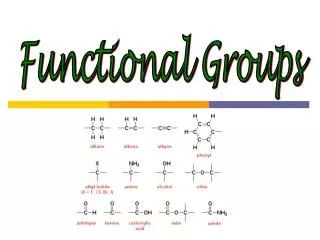
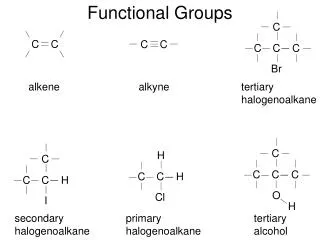
FUNCTIONAL GROUPS. MEMORIZE THEM : Figure 4.10 Hydroxyl •amino •methyl Carbonyl •sulfhydryl Carboxyl •phosphate ___________ makes them water soluble (hydrophilic) ____________makes them not water soluble (hydrophobic)

FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
FUNCTIONAL GROUPS • MEMORIZE THEM: Figure 4.10 • Hydroxyl •amino •methyl • Carbonyl •sulfhydryl • Carboxyl •phosphate • ___________ makes them water soluble (hydrophilic) • ____________makes them not water soluble (hydrophobic) • These functional groups are most likely involved in ______________________like dehydration synthesis, hydrolysis, etc.
Tuesday, October 8, 2013 • What are we doing today? • Finish Peer Teaching • Lipids and Carbohydrate notes • Homework: • REVIEW USING TARGETS, BOOK, AND WIKI Write all you know about a target to start!!! Use book and wiki to fill in the gaps.
SYNTHESIS & BREAKDOWN OF POLYMERS ENERGY IN ENZYMES ARE INVOLVED TO SPEED UP RATE OF RXN & LOWER RXN ACTIVATION ENERGY Monomers are joined to form polymers by _________________________(condensation) reactions Dehydration synthesis is a type of _________________!
SYNTHESIS & BREAKDOWN OF POLYMERS ENZYMES ARE INVOLVED TO SPEED UP RATE OF RXN & LOWER RXN ACTIVATION ENERGY ENERGY OUT Polymers are disassembled to form monomers by hydrolysis reactions Hydrolysis is a type of catabolism!
TARGET IV: MASTERY OF MACROMOLECULESCARBOHYDRATES = POLYSACCHARIDES I. Monomer unit = MONOSACCHARIDE A.General formula: CnH2nOn B. Most end in ________ C. Have carbonyl & hydroxyl groups D. Position of carbonyl group produces two classes of _______________________ : 1. ALDDOSE if carbonyl is at the END of C chain 2. KETONE if carbonyl is in the middle of C chain 3. See fig 5.3 E. Name of monosaccharide determined by # of carbons in chain: Hexose = ____, Pentose = _____, triose = ____
MORE MONOSACCHARIDE STUFF… • Structural isomers are common among monosaccharides and different structures imply… • Sugars in solution form rings(See figure 5.4) • Disaccharides are two monosaccharides joined by condensation reactions: a.k.a. dehydration synthesis(see figure 5.5) • Covalent bond between monosaccharides is called a____________________________ • Name examples of monosaccharides… • Name examples of disaccharides…
POLYSACCHARIDES • Functions of polysaccharides include… • Consist of ______________________to several thousand monosaccharides joined by … creating bonds called… • Function of polysaccharide is determined by type of monomer unit and position of glycosidic linkage • Plants produce _____________in two different forms: • Amylose (see figure 5.6a) • Amylopectin • How are forms similar? Different? • Animals produce & store CHO as _________________ in their liver (figure 5.6b)
MORE POLYSACCHARIDES… • How are plant and animal polysaccharides similar? Different? • Cellulose is a structural polysaccharide • Produced by plants, used in cell walls (figure 5.8) • Cellulose differs from starch in TWO ways: • ________________________________ • Isomer of glucose (fig 5.7a, b) • Different glycosidic bonds between glucose monomers make ________________ of cellulose polymer difficult • Can you digest cellulose? Why or why not? • Can a horse or other herbivores? How? • Ruminant digestion,sheep chew cud, too
LAST ONE FOR POLYSACCHARIDES… • Chitin is a structural CHO similar to cellulose with an extra N-containing appendage (figure 5.10) • Found in the exoskeleton of arthropods • Makes arthropods crunchy (and delicious) • Do you know the name of any arthropods?
LIPIDS Diverse group of macromolecules Some types of lipids DO NOT have ‘monomer’ unit building blocks ALL lipids, to some extent, are _______________ (water-fearing) and therefore have non-polar regions within their structure. What functional group(s) is (are) non polar? Examples: steroids, fats, & phospholipids
FATS (TRIGLYCERIDES) FIGURES 5.11 & 5.12 Function as long term energy storage. Where is the energy ‘stored’ in a fat polymer? Building blocks (monomers) are ______________(3C) and ________________(16-18C) Glycerol is joined to each fatty acid (at carboxyl group) by dehydration synthesis. How many dehydration events are required to make fat? Two types of fatty acids _________________- all carbons have single bond; animal fats = solid at room temp. (BUTTER, LARD, BACON GREASE) __________________- two carbons in chain joined by double bond; plant fats = liquid at room temp. (OLIVE OIL, CORN OIL)
PHOSPHOLIPIDS FIGURES 5.13 & 5.14 Major component of cell membranes Building blocks (_______________) are one hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails ___________________ ‘self-assemble’ when placed in water to form either a micelle OR a phospholipid bilayer