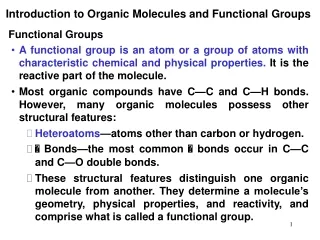
Functional groups
210 likes | 389 Vues
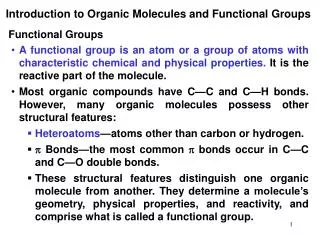
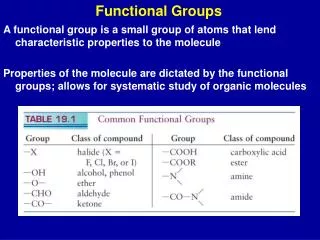
Functional groups. Carboxylic acid. C arboxylic acid is an organic compound that contains a carboxyl group They are used to make polymers, pharmaceuticals, solvents, and food additives Methonic acid- found in ant venom. Alcohol? .

Functional groups
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Carboxylic acid Carboxylic acid is an organic compound that contains a carboxyl group They are used to make polymers, pharmaceuticals, solvents, and food additives Methonic acid- found in ant venom
Alcohol? Alcohol is an organic compound which contains hydroxyl groups attached to a carbon atom. Uses include cleaning of wounds in medical situations, for beverages, fuel, and industrial use. Ethylene glycol is used as antifreeze
Ether Organic compound that has an ether group (an oxygen atom attached to two alkyl or aryl groups Anesthetic for surgeries and a solvent. Methyl etheris used in morphine
Ketone Ketones have a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms Used in industry and biology. Sugar and industrial products.
Aromatic Group Aromatic Group is a hydrocarbon with alternating double and single bonds. Used in industry and science Haphtalene- used in mothballs
Ester • Compound that has carbonyl next to an ether linkage • Widely in nature, used in industry • Make the aroma of many fruits • Examples apples, pears
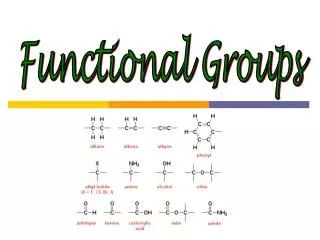
What is a carboxylic acid? • Carboxylic acid is an organic compound that contains a carboxyl group. • Used in the manufacturing of soap and rubber. • Also used in food and cold drinks • Ex: Acetic acid used to manufacture rubber.
What is an Alcohol? • Alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group is bound to a carbon atom • Used in beverages and cleaning agents. • Also used in disinfectants. • Example: Isopropyl- rubbing alcohol.
What is an Esther? • Esters are chemical compounds consisting of a carbonyl adjacent to an ether linkage. • More complex carboxylic acids • Used in scented candles. • Example: ethyl ethanoate-nail polish removed and decaf coffee.
What is a Ketone? • Ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. • Used in breaking down fat in the body. • Example: Formaldehyde- preserving animals.
What is an Ether? • Ethers are a class of organic compounds that contain an ether group — an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups — of general formula. • Used as anesthetics and used for mediums in radios. • Ex: Diethyl Ether – codeine
What is an Aromatic group? • An aromatic compound contains a set of covalently-bound atoms with specific characteristics. • Used in graphite, fuel, and cooking. • Ex: Graphene- single layer of graphite.
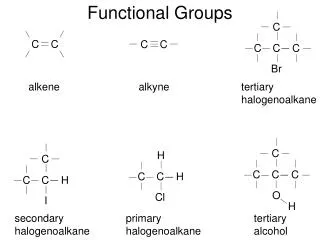
Carboxylic Acid • A carboxylic acid is an organic compound that contains a carboxyl group. • Carboxylic acids occur widely, and include the amino acids and acetic acid.
Alcohol • Alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group is bound to a carbon atom.
Ether • Ethers are a class of organic compounds that contain an ether group (an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups).
Ketone • A ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. • Ketones feature a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms.
Aromatic Group • Compound with alternating double and single bonds.
Ester • Esters are chemical compounds consisting of a carbonyl adjacent to an ether linkage.