Functional Groups
290 likes | 1.3k Vues
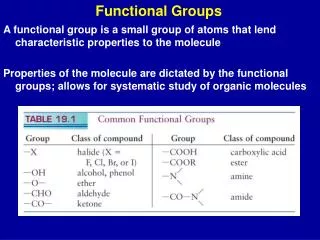
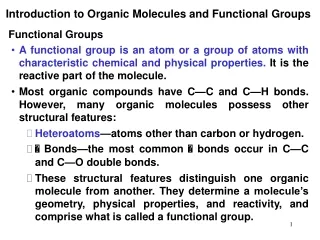
Functional Groups. A functional group is a small group of atoms that lend characteristic properties to the molecule Properties of the molecule are dictated by the functional groups; allows for systematic study of organic molecules. h n or heat. h n or heat.

Functional Groups
E N D
Presentation Transcript
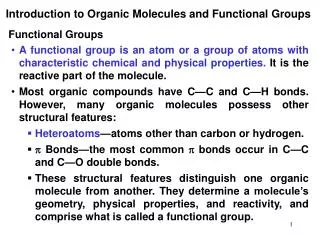
Functional Groups A functional group is a small group of atoms that lend characteristic properties to the molecule Properties of the molecule are dictated by the functional groups; allows for systematic study of organic molecules
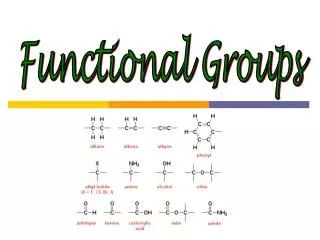
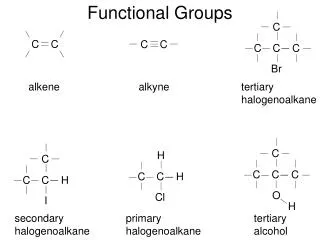
hn or heat hn or heat Halides: R-X where R is any alkyl group, and X a halogen CH3Cl - chloromethane C6H5Cl - chlorobenzene Synthesis: radical chain reaction between an alkane and a halogen CH4 + Cl2 CH3Cl + HCl Cl2 2Cl• •Cl + CH4 HCl + •CH3 •CH3 + Cl2 CH3Cl + •Cl
Primary alcohol Alcohols: R-OH hydroxyl functional group Nomenclature - use the suffix “ol” CH3-CH2-OH ethanol CH3-CH2-CH2OH 1-propanol Secondary alcohol Tertiary alcohol
Presence of OH group allows hydrogen bonding As the C chain becomes longer the OH group becomes less important Synthesis of alcohols Hydrolysis of a alkyl halide with a strong base OH- + CH3Br CH3OH + Br- Addition across a double bond CH2=CH2 + H2O CH3CH2OH Charge distribution in ethanol; red indicates negative charge 300 - 400oC 60 - 70 atm
Phenols: hydroxyl group attached directly to an aromatic ring Phenol (C6H5OH) weak acid, Ka = 1 x 10-10; stability of the phenolate ion (C6H5O-)
Oil of thyme Oil of clove
CH3-CH2-OH CH3-CH2-O-CH2-CH3 + H2O + 140oC CH3-CH2-OH H2SO4 180oC 2CH2=CH2 + 2 H2O H2SO4 H2SO4 Ethers: R - O - R C2H5 - O - C2H5 diethylether C6H5 - O - C2H5 ethylphenylether Synthesis: 2 R-OH R - O - R + H2O Kinetics vs thermodynamics
carbonyl group Aldehydes and Ketones aldehyde ketone HCHO: formaldehyde CH3CHO: acetaldehyde CH3COCH3: dimethlyketone (acetone)
O2, catalyst, high temperatures Properties of aldehydes and ketones differ because of the aldehyde H atom CH3CH2OH CH3CHO 1o alcohol aldehyde ethanol acetaldehyde (CH3)2CHOH (CH3)2CO 2o alcohol 2-propanol dimethylketone O2, catalyst, high temperatures
almond and cherries vanilla cinnamon
O2, Mn2+ HCOOH - formic acid (ant venom) CH3COOH - acetic acid (vinegar) Carboxylic acids hydrogen bond - “dimers” Synthesis Catalytic oxidation of aldehydes CH3CHO CH3COOH Carboxylic acids: -COOH functional group
Esters: R-COO- R’ acetic acid + ethanol ethylacetate
Fats (solids) and oils (liquids) are triesters formed from glycerol and three carboxylic acids (fatty acids) Tristearin: animal fatty acid tri-esters CH2OHCHOHCH2OH + 3 CH3(CH2)16COOH glycerol stearic acid Saturated - C-C single bonds Unsaturated - one (mono-unsaturated) or more (polyunsaturated) C=C bonds
ammonia Amines: primary amine (1o) secondary amine (2o) tertiary amine (3o)
CH3NH2 methylamine (CH3)2NH dimethylamine (CH3)3N trimethylamine C6H5NH2 aniline Amines are bases: NicH2+(aq) + 2 NH3(aq) Nic(aq) + 2 NH4+(aq) Synthesis of amines a) Naturally occurring b) NH3 + CH3Cl CH3NH2 + HCl nicotine
Amino acids: carboxylic acid containing an amine group Glycine: NH2CH2COOH
cationic form predominant in acidic solutions anionic form predominant in basic solutions dipolar form - zwitterion
Amides: -CONH2- group Formed by reaction between NH3 or 1o or 2o amine and acid
glycine + glycine diglycine + H2O Proteins: polypeptides with CONH linkage between amino acids http://www.cryst.bbk.ac.uk/pps97/course/section3/helix.pdb