Cell Structure and Function
370 likes | 390 Vues
Learn about the cell theory, cell structure, and cell function in this lecture. Discover the characteristics of cells, the functions of different organelles, and the endosymbiotic hypothesis. Explore the roles of the nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, and more. Enhance your understanding with a visual exploration of the inner life of a cell.

Cell Structure and Function
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Lecture 8b Cell Structure and Function
The Cell Theory All living things are composed of cells. All cells are derived from pre-existing cells, i.e., capable of reproduction Cells are the smallest unit of life
Characteristics of All Cells • A cell membrane encloses a fluid cytoplasm where most of the chemistry of the cell occurs. • DNA is the genetic code. • This genetic code is essentially the same for all cells. • The basic biological molecules and biochemical pathways are the same in all cells.
Tree of Life Eukaryote Prokaryote
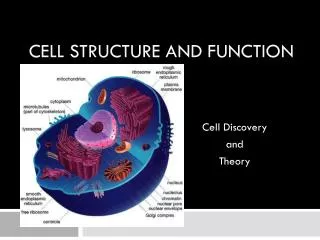
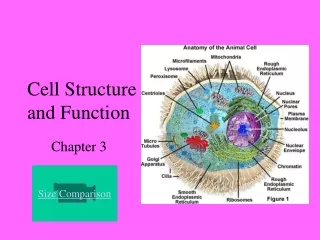
Eukaryotic Animal Cell Typical Animal Cell
Eukaryotic Plant Cell Typical Plant Cell
Membrane Functions Enclose cell Surround organelles Provide attachment sites Cell-cell recognition
Membrane Size & Structure Keeps things in/out Large area = more regulatory control Permits compartments Passing membrane may be important
highconcentration lowconcentration Compartments Isolate materials Concentrate materials Allow concentration gradients Diffusion membrane
Membrane Structure • Lipid bilayer • Highly motile • Life measured in hours • Embedded proteins • Life measured in days
Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough and Smooth ER
Ribosomes Make proteins
Mitochondria Respiratory center of cell
Function of the Golgi Complex Package and secrete products
Lysosome Function • Suicide sack • Digest food • Remove worn organelles
Endosymbiotic Hypothesis mitochondrion chloroplast
Mitochondria & Chloroplasts • Both are membrane bounded • Both are relatively large (bacterial size) • Endosymbiotic Hypothesis • Mutualistic relationship between different “organisms” • True?
Mitochondrion Very prominent Most cells have hundreds(plural: mitochondria) Powerhouse of the cell (fuel molecules to ATP)
Mitochondrion Metabolism Glucose (a sugar) to ATP ATP = universal energy “currency” ADP + energy ATP
Chloroplast Site of photosynthesis Similar to mitochondrion Even larger Produces organic compounds(these store energy)
Animal Vacuole Functions • Storage • Support • Water Regulation vacuole Plant mitochondria chloroplasts Both cell types havemembrane-bounded organelles
N Endosymbiosis Hypothesis A A prokaryote ingested some aerobic bacteria. The aerobes were protected and produced energy for the prokaryote A C B D Cyanobacteria Aerobic bacteria Chloroplasts Mitochondria N N Plant cell Prokaryote N Animal Cell
N Endosymbiosis Hypothesis B Over a long period of time the aerobes became mitochondria, no longer able to live on their own A C B D Cyanobacteria Aerobic bacteria Chloroplasts Mitochondria N N Plant cell Prokaryote N Animal Cell
N Endosymbiosis Hypothesis C Some primitive prokaryotes also ingested cyanobacteria, which contain photosynthetic pigments A C B D Cyanobacteria Aerobic bacteria Chloroplasts Mitochondria N N Plant cell Prokaryote N Animal Cell
N Endosymbiosis Hypothesis D Cyanobacteria became chloroplasts, unable to live on their own A C B D Cyanobacteria Aerobic bacteria Chloroplasts Mitochondria N N Plant cell Prokaryote N Animal Cell
Inquiry • What is the function of: • Mitochondria • Nucleus • Golgi apparatus • Lysozome • Ribosomes • Smooth and rough ER Cellular Visions: The inner life of a cell (video) http://www.studiodaily.com/main/searchlist/6850.html