Classification of Matter
130 likes | 262 Vues
Discover the basics of classifying matter into elements, compounds, and mixtures. Learn about atoms, compounds forming from elements, and different types of mixtures like solutions and suspensions. Understand the properties of homogenous and heterogenous mixtures, including colloids. Delve into the science behind the Tyndall Effect, a phenomenon used to identify colloid mixtures. Explore real-world examples to grasp the concepts of matter classification easily.

Classification of Matter
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What is matter? • Anything that occupies space and has mass
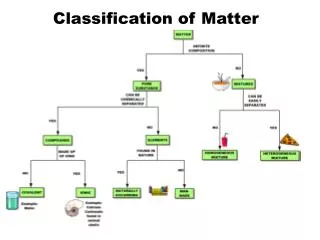
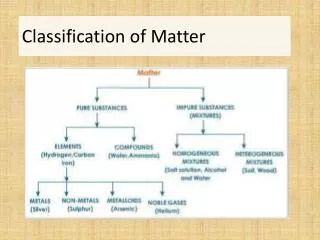
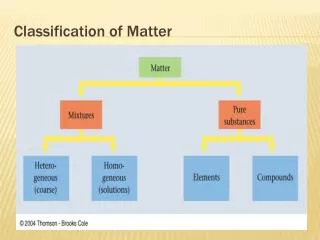
What is matter made of? • Substances: matter that is an element or a compound So how do we classify matter: - By the materials matter is made up of - 4 states of matter
Example: • How would you classify a pencil? - Wood - Graphite - Eraser Break it down to the to its simpler parts!!!!
Elements • The unit that makes up all matter are atoms • If all atoms of the sample of matter have the same identity they are called elements (see periodic table of elements) • Example: Oxygen
Compounds • What happens when two or more elements come together? • They form a Compound • Example: H20 • H is an element, O is an element, together they form the compound water
How about table salt? • Table salt is a compound: • NaCl • Na is an element, Cl is an element • Together they form a compound
Mixtures • What happens if you combine salt and water? • When you combine two or more substances that can be separated by physical means you have a mixture! • Salt can be separated from water by evaporation!!!
Back to the pencil! • The pencil is a MIXTURE: • Wood (compound) • graphite (element) • Eraser (compound)
Solutions • Salt water – mixture • Can you see the salt in the water? • No • Homogenous Mixture – • A material in which two or more substances are spread out evenly and cannot settle out when standing Homogenous mixture = Solution
Heterogenous Mixtures • A mixture in which different parts can be easily distinguished • Example: Pencil, Peanut Butter and Jelly Sandwich
Categories of Heterogenous Mixtures • Colloids – Heterogenous mixture that never settles • Example: Milk • How can you tell it’s a colloid? • By the Tyndall Effect • The scattering of light by the particles in the mixture
Suspension • Some mixtures are neither solutions nor colloids • They are known as a suspension • Is a heterogenous mixture containing a liquid in which visible particles settle out when standing • A muddy river • How is this different from a solution or colloid? - Particles carried in suspension will settle out