Understanding and Managing Red Eye Conditions: A Comprehensive Guide
170 likes | 302 Vues
This guide aims to help distinguish between acute eye emergencies and less urgent conditions, focusing on various causes of red eye, including acute conjunctivitis, keratitis, uveitis, and glaucoma. Key differences in symptoms, such as vision changes, pain, and discharge, are explored to aid diagnosis. Treatment options, including topical antibiotics, corticosteroids, and surgical interventions, are discussed. Accurate identification of red eye conditions is vital for effective management and preventing complications.

Understanding and Managing Red Eye Conditions: A Comprehensive Guide
E N D
Presentation Transcript
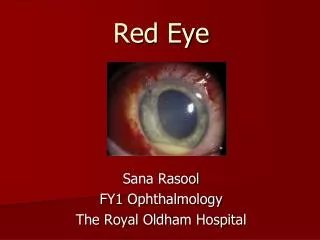
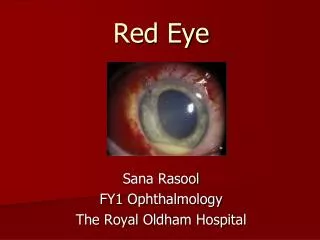
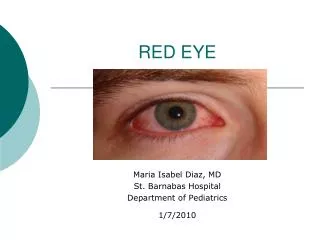
The red eye • Aim to distinguish acute emergency from less urgent • Vision affected? • Pain? • Unilateral/bilateral? • Distinguish conjunctival injection from ciliary flush
The red eye • Acute conjunctivitis • <3 weeks • Red eye • Discharge • Watery, mucoid, purulent • Irritation • Cornea clear • Vision good • Swab for culture+sensitivity • clean + topical antibiotic chloramphenicol
The red eye • Acute conjunctivitis • Papillae • Non specific • Except Giant papillae • atopic disease • Fb • Follicles • Physiologic in children • Chlamydia,adenovirus,herpes simplex, molluscum, drug toxicity, trachoma
The red eye • Bacterial conjunctivitis • Less common than viral • Conjunctival inflammation • Purulent discharge • Usually self limiting • Occasionally sight threatening • Gonococcal • Swab: Neonate,immunodeficient Severe cases Unresponsive cases
The red eye • Keratitis • Inflammation of cornea • Infection • Bacteria • Virus • Fungus • Protozoa • Dry Eye • Toxicity • Trauma • Chemical • Mechanical • UV light (arc eye) • loss of transparency • Reduced acuity • +/-pain
The red eye • Corneal ulcer • Emergency • scrape for Gram stain and culture • Intensive topical antibiotics • Fluoroquinolone • Fortified gentamicin and cefuroxime
The red eye • Corneal foreign body • Remove • Topical antibiotic • UV keratitis • History of welding • Cycloplegic + patch
The red eye • Uveitis • Inflammation of iris, ciliary body, choroid • Anterior uveitis • Pain • Sensitivity to light • Blurring • Ciliary flush • Deep AC • Clear cornea • But keratic precipitates • AC flare and cells • Irregular shape of pupil
The red eye • Uveitis • Topical steroid • Prednisolone 1% • Cycloplegia • Often recurrent • Chronic cases need investigation
The red eye • Herpes simplex keratitis • Discomfort • Watering • Photophobia • Ciliary flush • Dendritic pattern of fluorescein staining • Reduced corneal sensation • Recurrent disease
The red eye • Herpes simplex keratitis • Topical aciclovir • +/- debridement with sterile swab • Do NOT use steroid in epithelial disease • HSV can also affect stroma and endothelium which require steroid but these require close supervision
The red eye • Herpes zoster ophthalmicus • Reactivation of latent infection of trigeminal ganglion with varicella-zoster virus • Older age group • Can be triggered by malignancy, HIV, immunosuppression
The red eye • Herpes zoster ophthalmicus • Prodromal fever, malaise • Rash in dermatome • Vesicular, becoming crusty • Painful (maychronic) • Inflammation can affect ALL parts of eye • Lids, cornea, sclera, AC, uvea, optic nerve, cranial nerves • Can result in corneal opacity, new vessels
The red eye • Herpes Zoster ophthalmicus • Oral aciclovir 800mg x5 daily for 10 days starting WITHIN 72 hrs of onset • Topical ACV not indicated • Topical steroids and cycloplegia for stromal keratitis and uveitis • Need very slow taper • Respect this condition!
The red eye • Acute glaucoma • Pain • Blurring of vision • High IOP • Ciliary flush • Hazy cornea • Mid-dilated pupil • Shallow anterior chamber
The red eye • Acute glaucoma • Timolol 0.5% • Pilocarpine 1%-2% • Q15 minutes x3 • Prednisolone • Oral/iv Diamox • Beware CCF, renal disease • When acute attack broken perform laser or surgical iridotomy