Process Control Charts
150 likes | 793 Vues
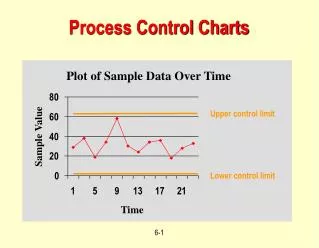
Plot of Sample Data Over Time. 80. Upper control limit. 60. Sample Value. 40. 20. Lower control limit. 0. 1. 5. 9. 13. 17. 21. Time. Process Control Charts. Control Charts. Process is not in control if: Sample is not between upper and lower control limits.

Process Control Charts
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Plot of Sample Data Over Time 80 Upper control limit 60 Sample Value 40 20 Lower control limit 0 1 5 9 13 17 21 Time Process Control Charts
Control Charts • Process is not in control if: • Sample is not between upper and lower control limits. • A non-random pattern is present, even when between upper and lower control limits. • Based on sample being normally distributed.
A Process in Control: • Two thirds of points are near the center line • A few points may be further out • Points float back and forth across the centerline at random • Points are balanced around the centerline • There are no, or few points outside limits • There are no patterns or trends.
Process capability (Ch.11) • Control charts measure what happens • Involves averages of samples • Specifications are what the customer wants • Involves individual units • Process capability: • How well can a process meet customer desires? • Can be subjective and changing.
Estimation of population stdev. • from raw data: • Sigma X can be calculated directly from individuals • Sigma Xbar = Sigma X / sqrt(n) • Estimate from sample Stdevs or Ranges: • Sigma X = Sbar /c4 or Sigma X = Rbar /d2 • C4 and d2 are factors from the Shewhart tables. Note all of these are estimates, and probably won’t agree exactly. • Process capability is 6-Sigma
Process capability is 6-Sigma • Capability Index related to Specification limits, USL and LSL: • Cp = (USL-LSL) / 6-Sigma • 6-Sigma < (USL-LSL) ; Cp>1 good situation • 6-Sigma = (USL-LSL) ; Cp =1 need center + control • 6-Sigma >(USL-LSL) ; more frequent failures even if centered and in control
Centering Index • Even if in control and good capability, must be centered at target value to give best results. • Cpk = Z(min) /3 where • Zmin = smaller of • Zusl = (USL-Xbar) / SigmaX • Zlsl = (Xbar-LSL) / SigmaX • Cpk = 1 if perfectly centered