Nucleotides and Amino Acids
200 likes | 315 Vues
This article explores the crucial relationship between structural biology and the functions of nucleotides and amino acids. Dr. Eric Wickstrom discusses how the triple helix and antiparallel B-form double helix of nucleic acids dictate biological processes. The role of ring stacking, hydrophobic repulsion, and hydrogen bonding in stabilizing these structures is examined. Additionally, the article highlights key features of amino acids, including aromatic properties and pK values, and details protein structures such as sperm whale myoglobin and prealbumin.

Nucleotides and Amino Acids
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Nucleotides and Amino Acids PR 613 Structural Biology I Dr. Eric Wickstrom
Nucleic Acids Triple helix Southern Northern
Antiparallel B-form (Southern) double helix Ring stacking and hydrophobic repulsion stabilize helix. Hydrogen bonds permit close approach, but don’t add stability!
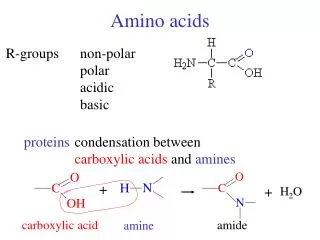
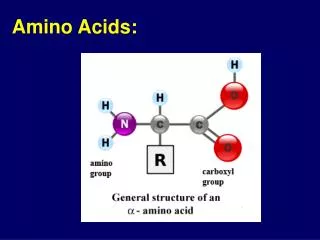
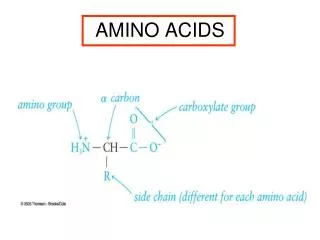
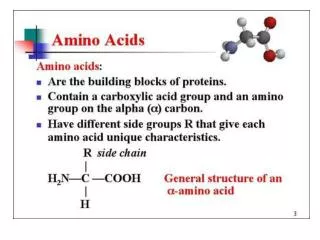
C to N, over the bridge Sidechain on the left in an L-amino acid
pK 10.5 pK 4 pK 4 pK 8
Sperm whale myoglobin a-helix 3.6 aa/turn 5.4 Å/turn 1.5 Å/aa 8 a-helices
Prealbumin b-sheet 2.0 aa/turn 7 Å/turn 3.5 Å/aa 16 b-sheets