Chapter 8 — The Nervous System
530 likes | 688 Vues
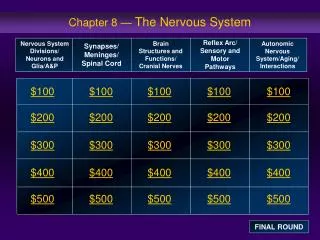
Chapter 8 — The Nervous System. Reflex Arc/ Sensory and Motor Pathways. Nervous System Divisions/ Neurons and Glia/A&P. Brain Structures and Functions/ Cranial Nerves. Autonomic Nervous System/Aging/ Interactions. Synapses/ Meninges/ Spinal Cord. $100. $100. $100. $ 100. $100. $200.

Chapter 8 — The Nervous System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 8 — The Nervous System Reflex Arc/ Sensory and Motor Pathways Nervous System Divisions/ Neurons and Glia/A&P Brain Structures and Functions/ Cranial Nerves Autonomic Nervous System/Aging/ Interactions Synapses/ Meninges/ Spinal Cord $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 FINAL ROUND
Topic 1:$100 Question • Which type of neuron is rare but occurs in special sense organs? • a. multicolor • b. univocal • c. bipolar • d. pseudounipolar ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 1:$100 Answer • Which type of neuron is rare but occurs in special sense organs? • a. multicolor • b. univocal • c. bipolar • d. pseudounipolar BACK TO GAME
Topic 1:$200 Question • Which of the following are collections of neuron cell bodies in the interior of the CNS? • a. nuclei • b. ganglia • c. centers • d. higher centers ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 1:$200 Answer • Which of the following are collections of neuron cell bodies in the interior of the CNS? • a. nuclei • b. ganglia • c. centers • d. higher centers BACK TO GAME
Topic 1:$300 Question • Changes in membrane potential that cannot spread far from the site of stimulation, thus affecting a limited portion of the plasma membrane, are called _________. • a. thresholds • b. action potentials • c. hyperpolarizations • d. graded potentials ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 1:$300 Answer • Changes in membrane potential that cannot spread far from the site of stimulation, thus affecting a limited portion of the plasma membrane, are called _________. • a. thresholds • b. action potentials • c. hyperpolarizations • d. graded potentials BACK TO GAME
Topic 1:$400 Question • Which of the following occurs along unmyelinated axons at a speed of about one meter per second? • a. nodal propagation • b. continuous propagation • c. hillock-centered propagation • d. saltatory propagation ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 1:$400 Answer • Which of the following occurs along unmyelinated axons at a speed of about one meter per second? • a. nodal propagation • b. continuous propagation • c. hillock-centered propagation • d. saltatory propagation BACK TO GAME
Topic 1:$500 Question • Bundles of CNS axons that share a common origin, destination, and function are called _______. • a. nerves • b. columns • c. tracts • d. pathways ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 1:$500 Answer • Bundles of CNS axons that share a common origin, destination, and function are called _______. • a. nerves • b. columns • c. tracts • d. pathways BACK TO GAME
Topic 2:$100 Question • A synaptic knob is as follows: • a. axon hillock of a presynaptic neuron • b. synaptic terminal of a postsynaptic neuron • c. proximal dendritic spine of a motor neuron • d. synaptic terminal of a presynaptic neuron ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 2:$100 Answer • A synaptic knob is as follows: • a. axon hillock of a presynaptic neuron • b. synaptic terminal of a postsynaptic neuron • c. proximal dendritic spine of a motor neuron • d. synaptic terminal of a presynaptic neuron BACK TO GAME
Topic 2:$200 Question • A mechanism for providing input to a single neuron from multiple sources is called ________. • a. serial processing • b. convergence • c. divergence • d. reverberation ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 2:$200 Answer • A mechanism for providing input to a single neuron from multiple sources is called ________. • a. serial processing • b. convergence • c. divergence • d. reverberation BACK TO GAME
Topic 2:$300 Question • The second meningeal layer is known as which of the following? • a. pia mater • b. dura mater • c. subdural space • d. arachnoid ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 2:$300 Answer • The second meningeal layer is known as which of the following? • a. pia mater • b. dura mater • c. subdural space • d. arachnoid BACK TO GAME
Topic 2:$400 Question • Regarding the spinal cord, cell bodies of sensory neurons are found in which of the following? • a. dorsal root ganglia • b. anterior white columns • c. ventral horns • d. dorsal horns ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 2:$400 Answer • Regarding the spinal cord, cell bodies of sensory neurons are found in which of the following? • a. dorsal root ganglia • b. anterior white columns • c. ventral horns • d. dorsal horns BACK TO GAME
Topic 2:$500 Question • In the spinal cord, visceral motor neurons that control smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands are found in the _________. • a. anterior gray horn • b. lateral white column • c. lateral gray horn • d. posterior gray horn ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 2:$500 Answer • In the spinal cord, visceral motor neurons that control smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands are found in the _________. • a. anterior gray horn • b. lateral white column • c. lateral gray horn • d. posterior gray horn BACK TO GAME
Topic 3:$100 Question • The network of permeable capillaries that extends into each of the four ventricles and are covered by ependymal cells that secrete CSF are called _________. • a. hypothalamus • b. epithalamus • c. choroid plexus • d. reticular system ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 3:$100 Answer • The network of permeable capillaries that extends into each of the four ventricles and are covered by ependymal cells that secrete CSF are called _________. • a. hypothalamus • b. epithalamus • c. choroid plexus • d. reticular system BACK TO GAME
Topic 3:$200 Question • The primary sensory cortex is found on the surface of the _________. • a. precentral gyrus • b. postcentral gyrus • c. temporal lobe • d. hippocampus ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 3:$200 Answer • The primary sensory cortex is found on the surface of the _________. • a. precentral gyrus • b. postcentral gyrus • c. temporal lobe • d. hippocampus BACK TO GAME
Topic 3:$300 Question • Which cranial nerve innervates the lateral rectus muscle of the eye? • a. Abducens Nerve (N VI) • b. Oculomotor Nerve (N III) • c. Optic Nerve (N II) • d. Trochlear Nerve (N IV) ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 3:$300 Answer • Which cranial nerve innervates the lateral rectus muscle of the eye? • a. Abducens Nerve (N VI) • b. Oculomotor Nerve (N III) • c. Optic Nerve (N II) • d. Trochlear Nerve (N IV) BACK TO GAME
Topic 3:$400 Question • Which cranial nerve is responsible for sensory innervation of the posterior third of the tongue? • a. Vagus Nerve (N X) • b. Facial Nerve (N VII) • c. Glossopharyngeal Nerve (N IX) • d. Hypoglossal Nerve (N XII) ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 3:$400 Answer • Which cranial nerve is responsible for sensory innervation of the posterior third of the tongue? • a. Vagus Nerve (N X) • b. Facial Nerve (N VII) • c. Glossopharyngeal Nerve (N IX) • d. Hypoglossal Nerve (N XII) BACK TO GAME
Topic 3:$500 Question • Damage to which area results in problems with estimating time relationships between events? • a. prefrontal cortex • b. hippocampus • c. amygdala • d. hypothalamus ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 3:$500 Answer • Damage to which area results in problems with estimating time relationships between events? • a. prefrontal cortex • b. hippocampus • c. amygdala • d. hypothalamus BACK TO GAME
Topic 4:$100 Question • A plantar reflex is also known as a/an _________. • a. positive Babinski reflex • b. reciprocal inhibition • c. negative Babinski reflex • d. Babinski sign ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 4:$100 Answer • A plantar reflex is also known as a/an _________. • a. positive Babinski reflex • b. reciprocal inhibition • c. negative Babinski reflex • d. Babinski sign BACK TO GAME
Topic 4:$200 Question • Which of the following is a motor pathway? • a. posterior column pathway • b. lateral pathway • c. spinothalamic pathway • d. spinocerebellar pathway ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 4:$200 Answer • Which of the following is a motor pathway? • a. posterior column pathway • b. lateral pathway • c. spinothalamic pathway • d. spinocerebellar pathway BACK TO GAME
Topic 4:$300 Question • Sensory neurons are also known as ____ neurons. • a. afferent • b. descending • c. efferent • d. effector ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 4:$300 Answer • Sensory neurons are also known as ____ neurons. • a. afferent • b. descending • c. efferent • d. effector BACK TO GAME
Topic 4:$400 Question • Axons of which neurons travel from the thalamus to the primary sensory cortex? • a. first-order neurons • b. second-order neurons • c. lower neurons • d. third-order neurons ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 4:$400 Answer • Axons of which neurons travel from the thalamus to the primary sensory cortex? • a. first-order neurons • b. second-order neurons • c. lower neurons • d. third-order neurons BACK TO GAME
Topic 4:$500 Question • The activities of pyramidal cells in the primary motor cortex are stimulated or inhibited by output from the _________. • a. basal nuclei and cerebellum • b. reticular system • c. thalamus • d. cerebellum and hippocampus ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 4:$500 Answer • The activities of pyramidal cells in the primary motor cortex are stimulated or inhibited by output from the _________. • a. basal nuclei and cerebellum • b. reticular system • c. thalamus • d. cerebellum and hippocampus BACK TO GAME
Topic 5:$100 Question • At about what age do age-related anatomical and physiological changes in the nervous system begin? • a. 45 years • b. 21 years • c. 30 years • d. 60 years ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 5:$100 Answer • At about what age do age-related anatomical and physiological changes in the nervous system begin? • a. 45 years • b. 21 years • c. 30 years • d. 60 years BACK TO GAME
Topic 5:$200 Question • Food processing and energy absorption are among functions of which of the following? • a. central nervous system • b. sympathetic nervous system • c. somatic nervous system • d. parasympathetic nervous system ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 5:$200 Answer • Food processing and energy absorption are among functions of which of the following? • a. central nervous system • b. sympathetic nervous system • c. somatic nervous system • d. parasympathetic nervous system BACK TO GAME
Topic 5:$300 Question • Norepinephrine and epinephrine are released by which of the following? • a. hypothalamus • b. adrenal medulla • c. pituitary gland • d. adrenal cortex ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 5:$300 Answer • Norepinephrine and epinephrine are released by which of the following? • a. hypothalamus • b. adrenal medulla • c. pituitary gland • d. adrenal cortex BACK TO GAME
Topic 5:$400 Question • Which is true regarding the effects of parasympathetic stimulation? • a. They are more localized and less specific than sympathetic effects. • b. They are less localized and less specific than sympathetic effects. • c. They are less localized and more specific than sympathetic effects. • d. They are more localized and more specific than sympathetic effects. ANSWER BACK TO GAME
Topic 5:$400 Answer • Which is true regarding the effects of parasympathetic stimulation? • a. They are more localized and less specific than sympathetic effects. • b. They are less localized and less specific than sympathetic effects. • c. They are less localized and more specific than sympathetic effects. • d. They are more localized and more specific than sympathetic effects. BACK TO GAME
Topic 5:$500 Question • Preganglionic parasympathetic fibers leaving the brain travel within which cranial nerves? • a. III, VIII, IX • b. VII, IX, X, XI • c. III, IX, X, XII • d. III, VII, IX, X ANSWER BACK TO GAME