Introduction to Earned Value Analysis
200 likes | 582 Vues
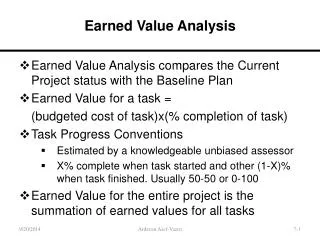
Introduction to Earned Value Analysis. What is Earned Value Concept. It is a technique for monitoring and tracking project progress. C/SCSC = Cost and Schedule Control System Criteria. It provides Cost and Schedule Integration. It was developed by Department of Defense. (DOD). B.

Introduction to Earned Value Analysis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Introduction to Earned Value Analysis
What is Earned Value Concept • It is a technique for monitoring and tracking project progress. • C/SCSC = Cost and Schedule Control System Criteria. • It provides Cost and Schedule Integration. • It was developed by Department of Defense. (DOD)
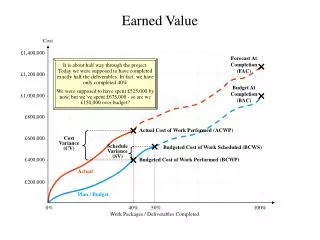
B actual budget time Traditional Barchart • Traditional Barchart and S-Curve provides comparison between actual progress and budget progress. • It does not provide accuracy comparison in term of time, cost separately. • It does not show reasons of project problems.
What is Earned Value Concept • Total project Budget is 1,000,000 Baht. • Total Project Duration is 10 Month. • We have passed 6 Months. • We have already spent 500,000 Baht, • What is our time status ? • What is our cost status ? • What should we do ? • If we got 55% work done.
B actual budget accomplishment or Earned Value (EV) time Something is added • Earned Value is added into the chart. • It means ‘earned quantity of work in term of money’ we get at the time. • Comparison between ‘earned ’ and ‘budget’ presents variance of time . • Comparison between ‘earned and ‘actual’ presents variance of cost.
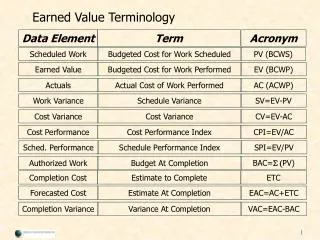
Earned Value Concept • Main Variables • BCWS - Budget Cost of Work Schedule =งานตามเป้าหมาย เราควรจะทำงานได้เท่าไรแล้ว ? มาจากการวางแผน • ACWP - Actual Cost of Work Performed =เงินที่จ่ายไปจริงคือเท่าไร ? มาจากการบันทึกทรัพยากรที่ใช้ไปจริง และเงินที่จ่ายสำหรับงาน • BCWP - Budget Cost of Work Performed =งานที่ทำได้จริง เราได้งานเท่าไร ? มาจากการวัดปริมาณงานที่ทำได้จริง
BCWP Measurement • Two types of Calculation • BCWP = % of Work CompletedxPlanned Cost per Percentage • BCWP = Quantity of Work done x Unit Cost of Work Planned. • งานที่ทำได้ = ร้อยละของงานที่เกิดขึ้น x ราคาต่อร้อยละของงาน • งานที่ทำได้ = หน่วยของงานที่ทำได้ x ราคาต่อหน่วยตามแผน
Schedule Variance (SV) • SV = BCWP - BCWS • SPI (Schedule performance index) = BCWP/BCWS • SVP (SV Percent) = SV x 100 / BCWS • You planned to finish task A in 10 days which total quantity is 10 unit. Schedule cost of the task is 1,000. After 10 days, you have got only 90% complete (9 units completed) • BCWS = 1000 • BCWP = 90 (%) x 10 (Baht/%) or = 9 (Units) x 100 (Baht per unit) = 900 • SV = BCWP - BCWS = 900-1000 = -100 • SPI = 900/100 = 0.9 • SVP = -100/1000 = -10% Behind Schedule.
schedule (BCWS) SV earned (BCWP) months behind Schedule Variance (SV) • SV = -100 • SPI = 0.9 • SVP = -10% Behind Schedule. • How much? • = 10% of the Period
Cost Variance (CV) • CV = BCWP - ACWP • CPI (Cost Performance Index) = BCWP/ACWP • CVP (CV Percent) = CV x 100 / BCWP • You planned to finish task A in 10 days which total quantity is 10 unit. Schedule cost of the task is 1,000. After 10 days, you have got only 90% complete (9 units completed). You have already spent 950. • BCWS = 1000 BCWP = 900 • ACWP = 950 • CV = BCWP – ACWP = 900-950 = -50 • CPI = 900/950 = 0.947 • CVP = -50/900 = -5.56% Cost Overrun
(CV and SV) CV, SV > 0 Good (Ahead or under run) = 0 OK - On Schedule., on budget < 0 Bad - Behind, overrun CVP, SVP > 0 Good (Ahead or under run) = 0 OK - On Schedule., on budget < 0 Bad - Behind, overrun CPI, SPI > 1 Good (Ahead or under run) = 1 OK - On Schedule., on budget < 1 Bad - Behind, overrun
B schedule actual CV SV earned time CV and SV
Example • Total budget (BAC) = 5000 • part way through project • Work scheduled (BCWS) = 2000 • Work accomplished (BCWP) = 1800 • Actual cost (ACWP) = 2400 • SV, SVP, SPI = ? • CV, CVP, CPI = ? • Report status of this project. • Recommend some actions.
positive variance zero schedule variance negative variance cost variance Trend Analysis
+10% 1.1 +0% 1.0 -10% 0.9 -20% 0.8 CPI CV% +10% 1.1 +0% 1.0 -10% 0.9 -20% 0.8 SV% SPI Trend Analysis
Cost Prediction • BAC = Budget at Completion งบประมาณทั้งหมดของโครงการที่วางแผนไว้ • ETC = Estimate to Complete ประมาณงบประมาณที่ต้องใช้ • ETC = ประมาณงบประมาณที่ต้องการต่อจากนี้ / CPI = (BAC - BCWP)/CPI • Previous example • ETC = (5000-1800)/CPI = 3200/CPI = ??
Cost Prediction • EAC = Estimate at Completion งบประมาณที่คาดว่าจะต้องใช้ทั้งหมดเมื่อจบโครงการ • EAC = ACWP + ETC = งบประมาณที่ใช้ไปแล้ว + ที่คาดว่าจะใช้ต่อไป • Previous example • EAC = ??
Time Prediction • ETTC = Estimate Time to Complete = ประมาณว่าจะใช้เวลาอีกประมาณเท่าไร= ปริมาณงานที่เหลืออยู่ / ((อัตราการทำงานตามแผน)* SPI) = (BAC- BCWP)/ ((Planned Working Rate)x SPI) • Previous Example, if planned time = 5 months • Working rate = 5000/5 = 1000 / Month • Then, estimated working rate = 1000*SPI • ETTC = (5000-1800)/(1000x SPI) = 3200/SPI = ?? • ETU (Estimate Time Use) = Time Use + ETTC • Do some exercises.