The Appendicular Skeleton
170 likes | 317 Vues
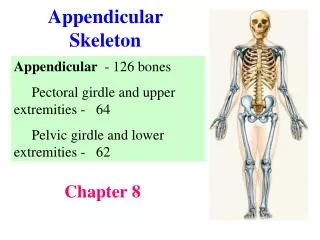
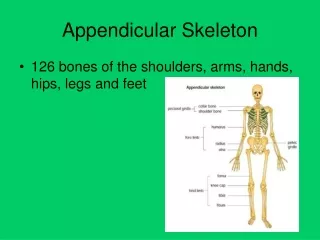
This chapter delves into the structure and function of the appendicular skeleton, focusing on the pectoral girdle comprised of the scapula and clavicle, which supports the upper limbs while allowing for mobility. Features of the humerus, ulna, and radius are discussed, alongside the details of the pelvic girdle, which provides trunk support and organ protection. The chapter outlines the important bones of the legs, including the femur, tibia, and fibula, and concludes with an overview of the foot bones, emphasizing their structural arrangement and roles.

The Appendicular Skeleton
E N D
Presentation Transcript
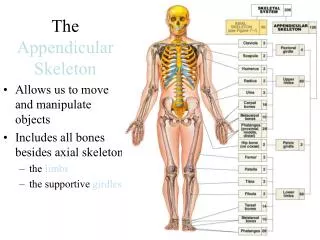
The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 7
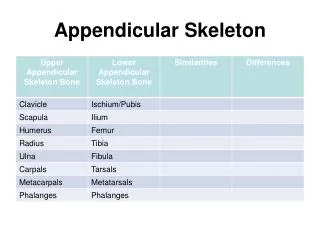
pectoral girdle = scapula (shoulder blade) + clavicle (collarbone)
Pectoral Girdle • supports the upper limbs, provides a place for muscle attachment • arrangement of bones good for mobility, but bad for stability
Features of the Scapula • glenoid cavity = depression where head of the humerus fits • acromionprocess = “point of the shoulder”
upper arm = humerus Features of the humerus • trochlea & capitulum = projections that articulate with ulna & radius
Lower arm = ulna & radius • radius is on thumb side of arm • ulna is longer and forms point of elbow
wrist = carpals • two rows, each with 4 short bones → 8 total
hand = 5 metacarpals (palm) and 14 phalanges (fingers) • Metacarpals numbered 1-5 starting from thumb side • phalanges numbered 1-5 starting from thumb side - fingers consist of 3 bones (proximal, middle, distal) and thumb 2 bones (proximal & distal)
pelvic girdle = 2 coxal bones • functions include support for the trunk, attachments for the lower limbs, protection for the bladder, large intestine, & reproductive organs
each coxal bone has 3 parts: • ilium: largest portion, iliac crest articulates with sacrum • ischium: lowest portion, you sit on the ischial tuberosities • pubis: anterior portion, fuses at the pubic symphysis
Features of the pelvis • acetabulum – cup-shaped region that articulates with head of the femur • obturator foramen- large opening where nerves & blood vessels pass from the spinal cord to the lower limbs
upper leg = femur • longest bone in body • articulates with coxal bone, tibia and patella
knee cap = patella • sesamoid bone • protects knee joint
lower leg = tibia (shin bone) and fibula • tibia: • larger of the 2 bones • on medial side of leg • articulates with the femur and tallus bone in the ankle • fibula • smaller bone • on lateral side of leg • bears no weight
ankle = 7 tarsals • talus (B) is only free moving bone of ankle • calcaneus / heel (A) is largest tarsal bone
sole/arch of foot = metatarsals • numbered 1-5 starting medially • weak arches → possible flat feet
toes = phalanges • 3 in each, except 2 in big toe • named same as phalanges in hand