The Fertile Crescent
140 likes | 447 Vues
The Fertile Crescent. Objective: - Explain how Mesopotamian civilization began and grew. - Explain and describe where one of the first civilizations arose. - Describe the early agricultural techniques of Mesopotamia. - Explain what an economic surplus is.

The Fertile Crescent
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Fertile Crescent Objective: - Explain how Mesopotamian civilization began and grew. - Explain and describe where one of the first civilizations arose. - Describe the early agricultural techniques of Mesopotamia. - Explain what an economic surplus is. - Explain why people settled in Mesopotamia.
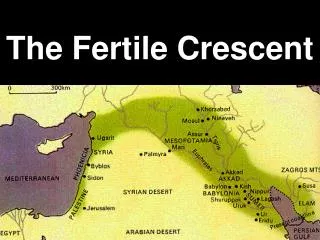
Where Civilization Began • Civilizations are groups of people who have a complex and organized society within a culture. • The first civilization began around 3500 B.C. • Each civilization has its own customs, food supply, social divisions, government, religion, and technology. • Civilization first developed in a crescent shaped area.
The Fertile Crescent • The region stretched from Mediterranean Sea to the Persian Gulf. • It was the land between the Tigris and the Euphrates River.
The Fertile Crescent Today • Today, the land of the Fertile Crescent is part of the countries of Iraq, Jordan, Syria, Lebanon, and Israel.
The Land of the Fertile Crescent • The forests of the fertile crescent provided a home for animals such as deer, sheep, and goats. • The grassland provided homes for wild pigs, oxen, and lions. • In the central area was a plain, or flat area of land, bordered by the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. • This area was known as Mesopotamia. • This means, “land between two rivers.”
Climate and Rivers • The climate was not ideal for farming. • Summers were long, hot, and dry with temperatures reaching 120°F. • Rainfall is inconsistent. • Because rainfall was inconsistent, the people had to figure out a way to get the water to their crops. • Irrigation – a system that helped people control when and where to water their crops. • Trenches and ditches brought water from the river to the fields.
The People • The people of Mesopotamia were problem solvers. • They made irrigation systems. • They made bricks out of mud, clay, and straw. • They then dried the bricks with the sun. • People used these bricks to build homes, temples, and palaces. • People worked as farmers and herders.
Growth of City – States and Trade • Once farming improved, people had time to build their villages. • Families and population began to grow. • Several villages included Uruk, Kish, Lagash, Nippur, Umma, and Ur. • These villages eventually became city-states. • A city-state is a city that is an individual unit, complete with its own form of government and traditions. • Some of the people were artisans, or craftspeople. • They were potters and weavers. • Some people also became traders. • This helped them get the natural resources they needed.
Time to Review • Where did the first civilizations arise? • What was the effect of the low rainfall in Mesopotamia? • What caused city-states to be established? • How did the Mesopotamian farmers use the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers to solve the problem of low rainfall? • How did Mesopotamian people get the natural resources they needed?