The Cell Cycle: Stages of Mitosis and Cytokinesis
510 likes | 530 Vues
Understand the different stages of the cell cycle, including interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis. Learn about the condensing and aligning of chromosomes, the role of centrioles and spindle fibers, and the division of the cytoplasm.

The Cell Cycle: Stages of Mitosis and Cytokinesis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
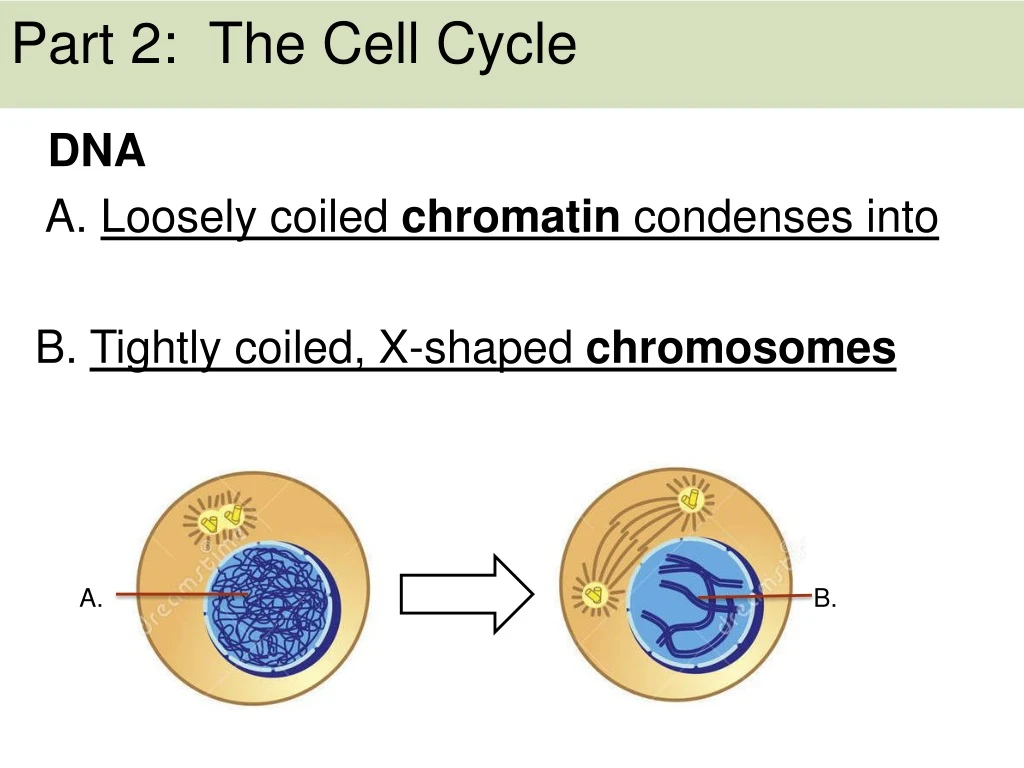
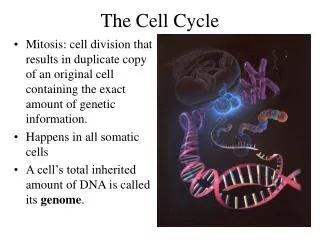
Part 2: The Cell Cycle DNA A. Loosely coiled chromatincondenses into B. Tightly coiled, X-shaped chromosomes A. B.
Chromatin is relaxed DNA Chromosomes are condensed DNA
6’ to microscopic supercoiled DNA
C. Part 2: The Cell Cycle CHROMOSOME C. Each half of the Xis called a sister chromatid Each sister chromatidcontains identical DNA
Part 2: The Cell Cycle D. CHROMOSOME D. Chromatids are held together by a centromere
Part 2: The Cell Cycle E. Centrioles – aid in cell division and are involved in the formation of spindle fibers F. Spindle Fibers – microtubules that push and pull sister chromatids for separation E. F.
Part 2: The Cell Cycle G. Poles – similar to the Earth’s poles, mitotic poles are at opposite “ends” of the cell, farthest from the equator H. Equator– plane on which chromosomes will align during metaphase G. H.
PROPHASE 1. The DNA condenses from chromosomes from chromatin 2. The nuclear membrane disappears 3. The centrioles form to move toward the poles 4. The spindle fibers form with ends moving toward the centromeres of the chromosomes
PROPHASE The DNA condenses from chromosomes from chromatin 2. The nuclear membrane disappears 3. The centrioles form to move toward the poles 4. The spindle fibers form with ends moving toward the centromeres of the chromosomes
METAPHASE The centrioles are at opposite poles 2. The chromosomes are aligned with their centromeres at the equator 3. The spindle fibers are stretched from centrioles to centromeres
METAPHASE The centrioles are at opposite poles 2. The chromosomes are aligned with their centromeres at the equator 3. The spindle fibers are stretched from centrioles to centromeres
ANAPHASE The spindle fibers shorten, pulling the sister chromatids apart 2. The sister chromatids move toward opposite poles
ANAPHASE The spindle fibers shorten, pulling the sister chromatids apart 2. The sister chromatids move toward opposite poles
TELOPHASE DNA: chromatids loosen, forming chromatin The centrioles and spindle fibers disintegrate The nuclear membrane reforms to enclose the DNA CYTOKINESIS 1. The cell membrane pinches as the cytoplasm is divided and the cell becomes 2
19. 5. 12. 20. 6. 1. 11. 2 [. 13. 3. 7. 4. 16. 8. 14. 21. 24. 18. 22. 17. 1. 10 [ 9. 15. 23.
Part 2: The Cell Cycle Cytokinesis Occurs in animal cells with a cleavage furrow
Part 2: The Cell Cycle Cytokinesis Occurs in plant cells with a cell plate
Part 2: The Cell Cycle Complete Homework 6-1 Read pgs 279-285
Section 6 – Cell Reproduction Part 2: The Cell Cycle
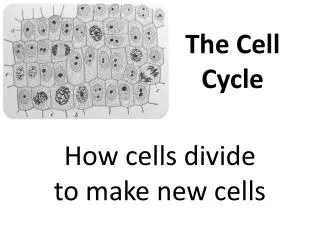
Part 2: The Cell Cycle Cells go through a life cycle that includes interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis
Part 2: The Cell Cycle Objectives: List / explain the primary stages of the cell cycle Describe the events of interphase Explain the four phases of mitosis Describe the process of cytokinesis
Part 2: The Cell Cycle The Cell Cycle Cells reproduce by a cycle of growing and dividingcalled the cell cycle
Part 2: The Cell Cycle The Cell Cycle Why would multicellular organisms need their cells to divide?
Part 2: The Cell Cycle The Cell Cycle Development of the embryo
Part 2: The Cell Cycle The Cell Cycle Growth
Part 2: The Cell Cycle The Cell Cycle Repair
Part 2: The Cell Cycle The Cell Cycle
Part 2: The Cell Cycle The Cell Cycle Each time a cell goes through a complete cycle, it divides into 2 cells
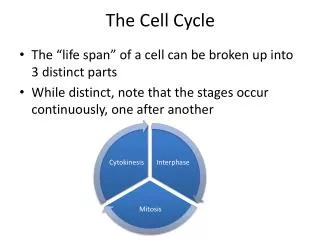
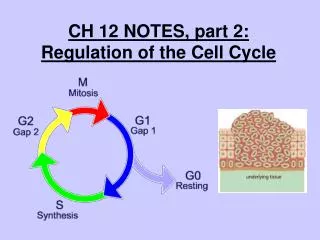
Part 2: The Cell Cycle The Cell Cycle There are three main stages of the cell cycle
Part 2: The Cell Cycle The Cell Cycle 1. Interphase
Part 2: The Cell Cycle The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis (division of nucleus)
Part 2: The Cell Cycle The Cell Cycle 3. Cytokinesis (Cytoplasm divides)
Part 2: The Cell Cycle Interphase Normal, healthy cells spend the majority of their time in interphase
Part 2: The Cell Cycle Interphase Interphase has three parts
Part 2: The Cell Cycle Interphase G1- (Gap 1) Cell growth
Part 2: The Cell Cycle Interphase 2. S - (Synthesis) DNA synthesized/replicated
Part 2: The Cell Cycle Interphase Why does the cell need to copy the DNA?
Part 2: The Cell Cycle Interphase 3. G2- (Gap 2) Cell prepares for mitosis
Part 2: The Cell Cycle Mitosis The cell’s replicated genetic material separates in Mitosis
Part 2: The Cell Cycle Mitosis Why is it important that the division of the nucleus occur equally?
Part 2: The Cell Cycle Mitosis Mitosis is divided into four stages:
Part 2: The Cell Cycle Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase
Part 2: The Cell Cycle Telophase and cytokinesis (the division of the cytoplasm) overlap.
Part 2: The Cell Cycle Mitosis *mnemonic*