Understanding Tangents and Secants: Circle Geometry Problems
180 likes | 286 Vues
This resource explores the relationship between line segments, tangents, and secants intersecting a circle. It provides practical problems involving the lengths of segments and the measures of angles formed by secants and tangents. Learn how to calculate missing lengths and angle measures with examples that cover different cases based on the vertex's location relative to the circle—inside, on, or outside. Ideal for students looking to deepen their understanding of circle geometry and related angle measures.

Understanding Tangents and Secants: Circle Geometry Problems
E N D
Presentation Transcript
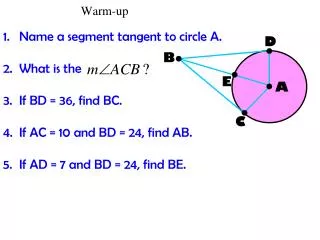
Name a segment tangent to circle A. • What is the • If BD = 36, find BC. • If AC = 10 and BD = 24, find AB. • If AD = 7 and BD = 24, find BE. Warm-up D B E A C
Unit Question:What happens when line segments intersect a circle? Today’s Question: How do you find the measure of angles formed by secant and tangent lines?
measure of an arc = measure of central angle m AB m ACB m AE A E 97 Q = 97° B C = 263° = 83°
Case I:Vertex is ON the circle ANGLE ARC ARC ANGLE
A secant line intersects the circle at exactly two points. SECANT sounds like second
Ex. 1 Find m1. A B 1 124° C m<1 = 620
Ex. 2 Find m1. 1 84° m<1 = 420
108° Ex. 3 Find m1. 1 m<1 = 1260
Case II:Vertex is inside the circle A ARC B ANGLE D ARC C Looks like a PLUS sign!
Ex. 4 Find m1. 93° A B 1 D C 113° m<1 = 1030
Ex. 5 Find mQT. mQT = 1000 N Q 840 920 M T
Case III:Vertex is outside the circle C ANGLE small ARC A D LARGE ARC B LARGE ARC LARGE ARC small ARC ANGLE small ARC ANGLE
Ex. 6 Find m1. 1 15° A D 65° B m<1 = 250
Ex. 7 Find mAB. m AB = 160 A 27° 70° B
Ex. 8 Find m1. 240° 1 m<1 = 600