Understanding Ionic Bonding: Formation, Characteristics, and Lattice Energy
100 likes | 235 Vues
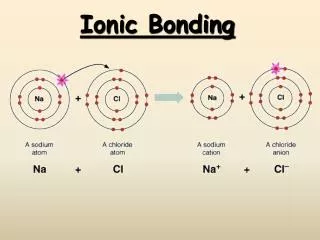
Ionic bonding occurs when electrons are transferred from an atom with low electronegativity to one with high electronegativity, resulting in the formation of cations (+) and anions (-) that are held together by electrostatic forces. The simplest ratio of these ions forms a formula unit, which shows the relationship of charges that balance to zero. Ionic compounds, commonly referred to as salts, arrange themselves in a crystal lattice structure, minimizing potential energy. Lattice energy, which indicates the strength of the ionic bond, is the energy released when one mole of the ionic compound is formed and is always a negative value.

Understanding Ionic Bonding: Formation, Characteristics, and Lattice Energy
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Formation of Bond • Electrons are transferred from an atom of low electronegativity to one of high electronegativity • Anion (-) and cation (+) formed • Opposite charges attract – called an electrostatic force
Formula Unit • Simplest ratio of atoms in an ionic compound • Charges combine to form a net of zero • Formulas are not molecules: they do not show exact numbers of atoms just ratios • Another term for an ionic compound is salt
Example • Show how the bond forms in each pair and tell the formula unit Ca and F K and O Al and O
Ions Arrangement • Opposite ions arrange themselves with each positive ion surrounded by negative ions and each negative surrounded by positive ions • Where potential energy is lowest • This arrangement is called a crystal lattice
Lattice Energy • Energy released when one mole of an ionic compound is formed from its ions • Values will always be negative, because energy is released • The larger the negative value for the lattice energy, the stronger the ionic bond in the crystal is
Lattice energy Compound(kJ/mol) NaCl −787.5 NaBr −751.4 CaF2 −2634.7 CaO −3385 LiCl −861.3 LiF −1032 MgO −3760 KCl −715