Investigating the Role of S100A7 and EGF in T47D Cell Migration and Invasion
30 likes | 148 Vues
This study explores the impact of S100A7 and EGF on cell migration and invasion in T47D cells. We present supplementary figures demonstrating cell migration metrics under various conditions, including S100A7 expression and EGF stimulation. Key signaling pathways involving EGFR, LIMK-1/2, Rac-1, and NF-KB are analyzed, with a focus on how S100A7 interacts with ERα to regulate MMP-9 activity. Findings suggest that S100A7 plays a crucial role in invasive behavior, providing insights into cancer cell motility mechanisms.

Investigating the Role of S100A7 and EGF in T47D Cell Migration and Invasion
E N D
Presentation Transcript
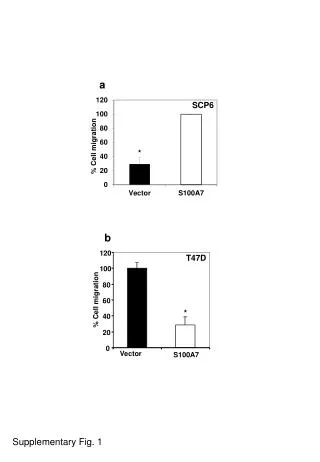
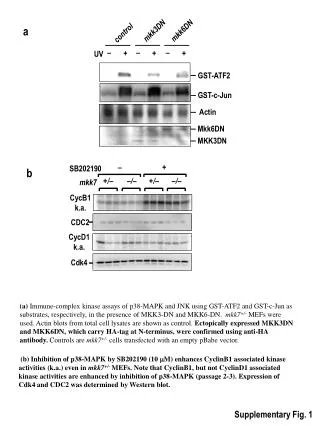
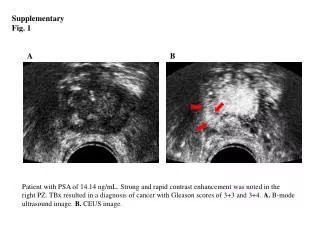
a b 120 T47D 100 80 % Cell migration 60 * 40 20 0 Vector S100A7 SCP6 % Cell migration * Supplementary Fig. 1
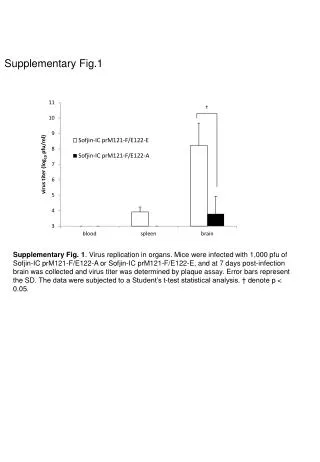
T47D 30 Vector S100A7 20 % Invasion * 10 * 0 -EGF +EGF Supplementary Fig. 2
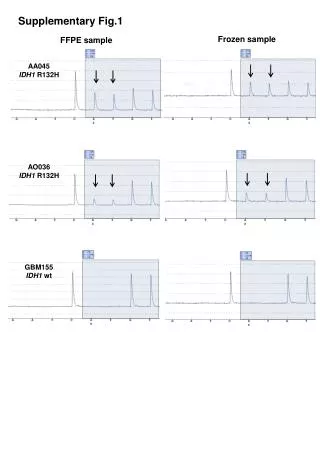
EGF EGFR LIMK-1/2 Active Rac-1 GTP S100A7-ERα- Migration p-Cofilin F-actin G-actin N p-p65-NF-KB ATP NF-KB binding site S100A7-ERα+ MMP-9 Invasion LIMK-1/2 MMP-9 Active Rac-1 MMP-9 Invasion Migration Supplementary Fig. 3