Understanding Digital Circuits and Signals: Noise Margins, Logic Conversion, and Binary Operations
160 likes | 257 Vues
Learn about noise margins, logic circuits, binary conversion, BCD, hexadecimal representation, and binary addition. Understand two’s complement, binary numbers, and subtraction.

Understanding Digital Circuits and Signals: Noise Margins, Logic Conversion, and Binary Operations
E N D
Presentation Transcript
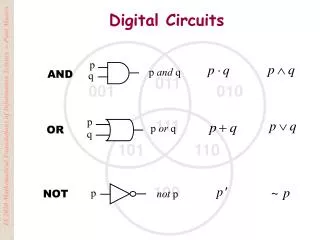
VM Noise margins in Logic Circuits
VDD "1" V OH Noise margin high NM H V IH Undefined Region V NM Noise margin low L IL V OL "0" VGND Gate Input Gate Output Noise margins in Logic Circuits
Digital to Binary Conversion Conversion of the integer part
Digital to Binary Conversion Conversion of the fractional part
A B A B A B A B 0 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 C C C C C i ,0 o ,0 o ,1 o ,2 o ,3 FA FA FA FA = ( C ) i ,1 S S S S 0 1 2 3 Binary Addition A B C One bit binary adder Sum Carry
Binary Coded Decimal and Hexadecimal Representation To get BCD replace each digit by a group of 4 bits 3786.1=0011 0111 1000 0110. 0001BCD Binary to hexadecimal conversion (0,1,..9,A,..,F) 1110 1010 1001 0101=EA9516 Exercise: Represent 25 by its BCD and binary codes
Binary Coded Decimal and Hexadecimal Representation To get BCD replace each digit by a group of 4 bits 3786.1=0011 0111 1000 0110. 0001BCD Binary to hexadecimal conversion (0,1,..9,A,..,F) 1110 1010 1001 0101=EA9516 Exercise: Represent 25 by its BCD and binary codes 25/2 = 12 rem 1 12/2 = 6 rem 0 6/2 = 3 rem 0 3/2 = 1 rem 1 1/2 = 0 rem 1 25 = 0010 0101BCD 25 = 0001 1001
Two’s Complement and Binary Addition One’s complement id obtained by inverting all the bits Two’s complement is obtained as one’s complement + 1 invert
Positive and Negative Binary Numbers Signed two’s complement of a number is used a the negative number value. This can be used in subtraction operation.
Positive and Negative Binary Numbers This can be used in subtraction operation. To subtract number B from A we add two’s complement of B to A • Example: Compute A-B=25-11 using binary adders • Find binary representations A= , B= • Find two’s complement of B -B= • Add A+(-B) using binary notation
Positive and Negative Binary Numbers This can be used in subtraction operation. To subtract number B from A we add two’s complement of B to A • Example: Compute A-B=25-11 using binary adders • Find binary representations A=011001, B=001011 • Find two’s complement of B -B=110101 • Add A+(-B) using binary notation • 011001 • +110101 • 001110 = 14