CELLS
450 likes | 679 Vues
CELLS. Chapter 7.1. CELL BIOLOGISTS. Anton van Leeuwenhoek - Dutch lens maker who developed the first simple microscope. CELL BIOLOGISTS. Robert Hooke - English scientist. First coined the word “cells” after looking at cork . CELL BIOLOGISTS.

CELLS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CELLS Chapter 7.1
CELL BIOLOGISTS • Anton van Leeuwenhoek - Dutch lens maker who developed the first simple microscope
CELL BIOLOGISTS • Robert Hooke - English scientist
First coined the word “cells” after looking at cork.
CELL BIOLOGISTS • Matthias Schleiden - German Botanist who studied plant cells
CELL BIOLOGISTS • Theodor Schwann - German Zoologist - studied animal cells
CELL BIOLOGISTS • Rudolf Virchow • German physician • New cells could be produced only from the division of existing cells rudolfvirchow.net/
The cell is the basic unit of structure and function 3. Cells come from other cells
TYPES OF CELLS • Prokaryotic - cells with no nucleus or membrane bound organelles • very simple cells • bacteria, some blue-green algae
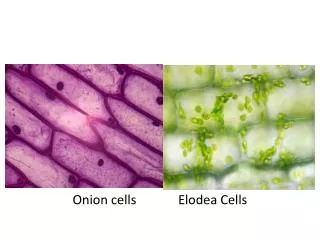
Eukaryotic - cells with a nucleus and membrane bound organelles • complex cells • animal, plant, fungi, protist
Unicellular Organisms • ONE- celled organisms which • Grow • Respond to environment • Transform energy • Reproduce • Ex: Volvox aureus www.volvoxaureus.com/volvox.htm
Multicellular Organism • Organisms made up of MANY cells • Different kinds of cells are SPECIALIZED to perform particular functions within the organism • Ex: muscles cells, nerve cells, guard cells, red blood cells…
Levels of Organization • Observed in Multicellular Organisms • Cells- of similar type work together to form • Tissues- grouped together to form • Organs- work together as part of • Organ System- group of organs working together to perform a specific function • Organism- all systems working together
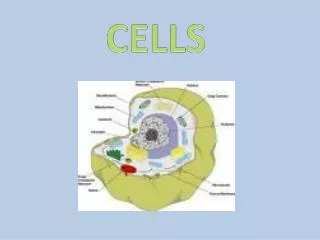
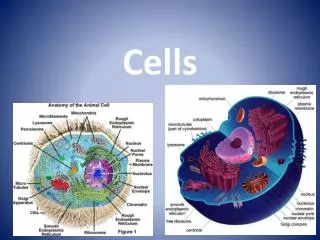
CELL STRUCTUREPlasma Membrane • selectively permeable • separates cell from its environment • composed of lipid bilayer with embedded proteins
CELL STRUCTURENucleus • surrounded by nuclear envelope • contains genetic information (chromosomes), • “brain” of the cell
Nucleolus • Inside the nucleus • Makes ribosomes
CELL STRUCTURECytoplasm • Composed mostly of water • Has salts, sugars, proteins and other materials suspended in it • Colloid consistency
CELL STRUCTURESOrganelles - Mitochondria • Powerhouse of the cell • Contains its own DNA • Can reproduce when cell energy demands increase • Converts glucose to other energy forms
The Mighty Mitochondria
Chloroplast • Only in plant, algae, and some bacterial cells • Convert the sun’s energy to glucose • Composed of “solar collectors” called grana • Contain chlorophyll pigment
Ribosomes • Protein manufacturing site • Young cells have many more than older cells
Endoplasmic Reticulum • Network of tubes that transport materials within the cell and to the cell surface for release • smooth and rough e.r.
Smooth ER • Manufactures and transports lipids within the cell
Rough E.R. • Rough in appearance due to presence of ribosomes • Manufactures and transports proteins to cell surface for release
Golgi Apparatus • Packages and processes cellular materials and prepares them for shipment
Lysosome • Site of cell digestion • Contains digestive enzymes • Called “suicide sacs” • Responsible for cell destruction
Vacuole • Used by cells to store nutrients, wastes, and cellular products; water storage
Vesicles • Used by cells to temporarily store cellular products (such as hormones and enzymes) before release from the cell
Centrioles • Found only in animal cells • Used during cellular reproduction to help separate chromosomes evenly
Cytoskeleton • Protein filaments which act as scaffolding to support cellular components • Major component of cilia and flagella
Cilia and Flagella • Structures used for locomotion of organism or transportation of materials
Plastids • Found only in plant cells • Used to store plant materials • Chromoplasts - color • Chloroplasts – chlorophyll • Leucoplasts – starch
Cell Wall • Found in plants, fungi, and some bacteria • NOT found in animal cells • Made of cellulose, chitin or some other carbohydrate • Rigid, provide strength, support, protection • Like armor for the plant cell