Cells
370 likes | 631 Vues
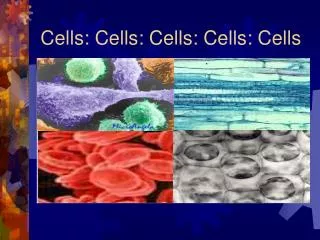
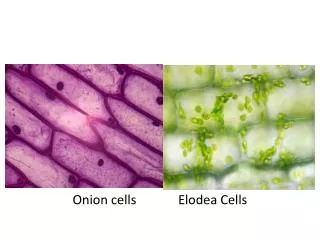
Cells. Molecular Biology Techniques. Which type of cell has a nucleus?. Prokaryotic Eukaryotic. Eukaryotic versus Prokaryotic Cells. Prokaryotic - Cells lacking a nucleus. Eukrayotic - Cells containing a nucleus. Organelles - Membrane-bound bodies found within eukaryotic cells.

Cells
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Cells Molecular Biology Techniques
Which type of cell has a nucleus? • Prokaryotic • Eukaryotic
Eukaryotic versus Prokaryotic Cells • Prokaryotic - Cells lacking a nucleus. • Eukrayotic - Cells containing a nucleus. • Organelles - Membrane-bound bodies found within eukaryotic cells.
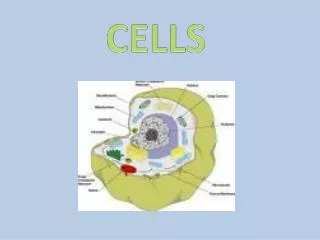
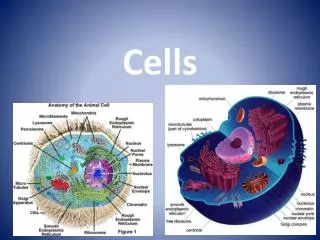
Cell Structure • Cell wall: Rigid boundaries of the cell • Cellulose: organic compound that makes up the majority of plant cell walls • Cotton is 90% cellulose • Hemicellulose: Gluelike substance that holds cellulose fibers together within the wall • Pectin: Organic matter that provides stiffness
Cell Structure • Cell (Plasma) Membrane: Binds all the living components within the protoplasm • Cytoplasm: All cellular components between the plasma membrane and the nucleus
What is the name of the jelly like substance where many chemical reactions take place and cell organelles are embedded? • Cytoplasm • Chloroplast • Nucleus • Cellulose
Nucleus • Nucleus: Control center of the cell, houses DNA, DNA provides information needed to fulfill the cells’ needs (growth, differentiation, etc) & stores heredity information • Nuclear Envelope: Structurally complex pores, proteins that act as channels for molecules are within the pores, acts as gatekeeper between nucleus and rest of cell • Chromatin: Composed of proteins and DNA, when nucleus divides for mitosis, chromatin coils. • Chromosomes: Condensed condition of chromatin. Each plant/animal cell has its own fixed number of chromosomes, radish has 18, humans have 46.
What controls reproduction and contains the genetic info of the cell? • Cell wall • Nucleus • Nuclear envelope • Plastids
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) • Endoplasmic Reticulum facilitates cellular communication and materials channeling. • Connected to outer membrane of nucleus • Rough ER distributes ribosomes • Smooth ER associated with lipid secretion
Ribosomes • Ribosomes are composed of two subunits composed of RNA and proteins. • involved in linking amino acids for the construction of large protein molecules
Golgi apparatus • are often bound by branching tubules that originate from the ER. • Involved in the modification of carbohydrates attached to proteins synthesized and packaged in the ER.
Plastids • Plastids: associated with the storage or manufacturing of carbohydrates • Chloroplasts: Location of photosynthesis, contain stacks of grana • Grana/Granum: contain thylakoids • Thylakoids: contain chlorophyll • Chlorophyll: give green pigment • Chromoplasts • Found in colored plant organs, like fruits & petals. • Some chloroplasts evolve into chromoplasts (like ripening tomatoes). • Leucoplasts • No pigment, assumed to be in roots. • May become specialized for bulk storage of starch, lipid or protein.
What is the location of photosynthesis in the cell? • Plastids • Chloroplast • Chromoplasts • Leucoplasts
What gives plants their green pigment? • Grana • Thylakoids • Dictyosomes • Chlorophyll
Mitochondria • Mitochondria release energy produced from cellular respiration. • Powerhouse of the cell
Glycolysis Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Chain H2O
Vacuoles • Used for storage in plants • In mature cells, 90% of volume may be taken up by central vacuoles bounded by vacuolar membranes. • Filled with cell sap which helps maintain pressure within the cell. • Also frequently contains water-soluble pigments, like anthocynaninwhich provide color for flowers.
Cytoskeleton • Cytoskeleton is an intricate network of microtubules and microfilaments. • Microtubules control the addition of cellulose to the cell wall.
Summary • Cytoplasm Jelly like substance where chemical reactions take place and other parts are embedded. • Nucleus Controls reproduction and also contains the characteristics of the cell. • Cell membrane Surrounds the cell and controls what moves in and out of the cell. • Mitochondria Found only in plant cells where respiration occurs. • Chloroplasts These makes plants green. They contain chlorophyll which is needed for photosynthesis.
What gives cells their shape? • Cell wall • Cell membrane • Sap • Vacuoles
Summary • Cell wall Gives the cell its shape. The cell's "skeleton". • Vacuole Where the cell sap is stored, controls pressure • Golgi Apparatus Involved in the modification of carbohydrates attached to proteins synthesized • Endoplasmic Reticulum Facilitates cellular communication and materials channeling, distributes ribosomes • RibosomesInvolved in protein synthesis
Cellular Reproduction • Cell division process referred to as cell cycle. • Divided into interphase and mitosis. • Interphase • Period when cells are not dividing. • G1 - Cell increases in size. • S - DNA replication takes place. • G2- Mitochondria divide, and microtubules produced. • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O3_PNiLWBjY
Mitosis • Mitosis refers to the process of cellular division that produces two daughter cells with equal amounts of DNA and other substances duplicated during interphase. • Each daughter cell is an exact copy of the parent cell. • Mitosis occurs in meristems.
Prophase • Chromosomes condense. • Strands of chromatin coil and tighten with centromeres holding each pair of chromatids together. • Nuclear envelope fragments.
Metaphase • Chromosomes align at the cell’s equator. • Spindle fibers collectively referred to as the spindle. • At the end of metaphase, the centromeres holding each sister chromosomes separate lengthwise.
Anaphase • Sister chromatids separate and are pulled to opposite poles. • Spindle fibers gradually shorten as material is continuously removed from the polar ends.
Telophase • Each group of daughter chromosomes become surrounded by a nuclear envelope. • Daughter chromosomes become indistinguishable. • Nucleoli reappear • Spindle fibers disintegrate • Cell plate forms.
Mitosis in Action • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VlN7K1-9QB0&feature=related • http://www.youtube.com/watch?annotation_id=annotation_706798&v=VGV3fv-uZYI&feature=iv