Cells
250 likes | 264 Vues
Learn about the different parts of animal and plant cells, their functions, and the importance of specialized cells. Discover how cells form tissues, organs, and organ systems in living organisms. Explore various systems in the body and their roles.

Cells
E N D
Presentation Transcript
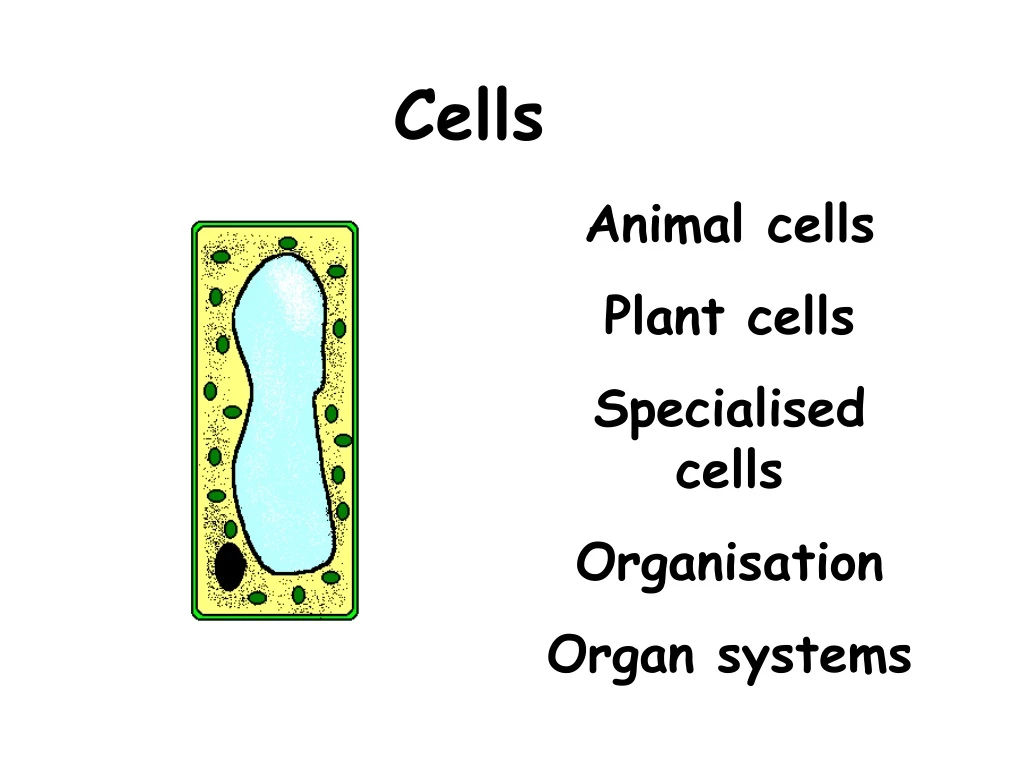
Cells Animal cells Plant cells Specialised cells Organisation Organ systems
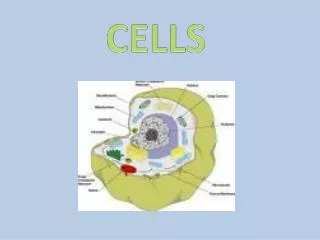
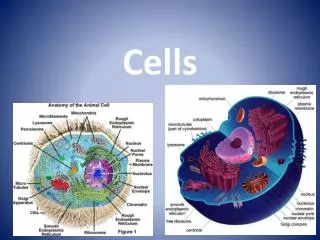
Exercise 1: Label the Animal Cell B. _________ Cytoplasm C. ____________ Cell membrane A. ________ Nucleus
Exercise 2: Label the Plant Cell B. _______ Vacuole C. __________ Cytoplasm D. __________ Chloroplast A. ________ Cell wall
Exercise 3: Link the Word with the Description Controls what enters and leaves the cell Vacuole Chloroplast Controls the cell Contains cell sap Cytoplasm Supports plant cells and is made of cellulose Cell wall Absorbs sunlight for photosynthesis Cell membrane Where chemical reactions occur Nucleus
Which part of the cell controls the cell? • What happens in the cytoplasm? • What does the cell membrane do? • Which three parts are in plant and animal cells? • Which three parts are only found in plant cells? The nucleus. Where chemical reactions occur. Controls what enters and leaves the cell, gives the cell shape. Nucleus, cytoplasm and cell membrane. Vacuole, cell wall and chloroplasts.
Why do cells have different shapes? Are all cells the same shape ?
Specialised Cells 1 The sperm cell is adapted to its function by being streamlined and having a tail so it can swim. A sperm cell The leaf palisade cell has a large surface area for efficient gas exchange. It also has lots of chloroplasts to absorb sunlight for photosynthesis. A leaf palisade cell
Specialised Cells 2 The red blood cell is adapted to its function by having a large surface area for efficient absorption of oxygen. A red blood cell The ciliated cell has tiny hairs that filter out dust from the air you breathe and move mucus along as well. Ciliated cell
Exercise 5: Link the Cells with the Diagram B. D. C. A. Palisade cell Ciliated cell Red blood cell Sperm cell
No Do cells work on their own? What is the name given to a group of similar shaped cells that do they same job ? Tissues A ciliated epithelial cell What is their function? Ciliated epithelial tissue in a lung
Cells to Tissues Muscle tissue Muscle cell Nerve cell Nerve tissue
Special cells found in plants A root hair cell takes in water Root hair tissue Palisade cells are packed with chloroplasts to help the plant make food Palisade tissue
Work to do • 1. Use page 10 a& 11 to complete the worksheet, ‘Special cells’, by writing the answers on the sheet. Then stick the worksheet in your book. • 2. Complete the worksheet 7Ad/4 Tissue matching and stick it in your book.
All systems go Muscle cells are grouped to form muscle tissue The heart contains muscle and nerve tissues Nerve cells are grouped to form nerve tissue
Root hair cells are grouped together to form root hair tissue The root contains root hair and xylem tissue
How do we get new cells? The nucleus splits into two A new cell membrane forms in the middle The new daughter cells get bigger. Once the daughter cells are full size, they can too can divide
1. Put the title New cells • 2. Answer questions 3 & 4 from page 13
7Ac/5 Odd cell out Look at each set of cells. Work out what each cell is and what it does (its function). Then decide which is the odd one out. For example are they plant or animal cells? Do they have different structures in the cells??
Exercise 6: Match the Words and Diagrams Cell Tissue Organ Organ system
Exercise 10: Name the Systems B. C. D. A. Digestive Skeletal Respiratory Excretory