CELLS
180 likes | 345 Vues
CELLS. 06/18/12. What is a cell?. The Cell Theory : 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and functions in living things. - Bone cells make up bones. - Nerve cells transmit signals from brain to rest of body.

CELLS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CELLS 06/18/12
What is a cell? • The Cell Theory: 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and functions in living things. - Bone cells make up bones. - Nerve cells transmit signals from brain to rest of body. 3. All cells come from preexisting cells. - Cells replicate to form other cells.
Types of Cells • Nerve Cells: They are responsible for relaying information from your brain to your muscles, organs, and other parts of your body. • Muscle Cell: Important for the contraction of muscles. • Skin Cell: Builds your skin. Protects from the outside world • What other cells can you think of?
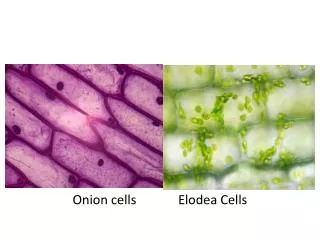
Onion Root Skin Cells Nerve Cells
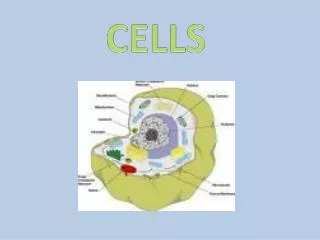
Organelles • Organelles are the organs of cells. “Little organs”. • There are many different organelles, all having a specific function. Remember to take good notes! WE WILL LEARN A LOT OF ORGANELLES
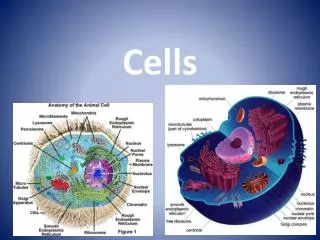
Basic Cell Structure Cell Membrane: Serves as the outer boundary of the cell. It regulates what can and cannot enter the cell. Cytoplasm: The space between the nucleus and the cell membrane. Contains many different organelles. Nucleus: Main control center. Directs all activities of the cell. This is where the DNA is.
Mitochondria • This is the “power plant”. • This is where the carbohydrates and lipids are broken down to release their energy.
Ribosomes • Among the smallest of organelles. • There are many of these in a cell. • This is where protein is made.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) • Looks like a long tunnel system. • Can either be rough or smooth • Rough if ribosomes are attached to it. • The ER transports materials through the inside of the cell. • Transports the proteins!
Golgi Apparatus • This is the “shipping” organelle. • The post office for proteins • Looks like a stack of pancakes. • The Golgi modifies proteins, much like we modify cars, and then sends them to other parts of the cell where they can do specific functions.
Lysosomes • Contain chemicals and proteins (enzymes) necessary for digesting certain materials in the cell. • The “clean-up crew” • Formed from Golgi
Vacuoles • Store materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates. • Think of a refrigerator or a pantry that stores food. • They look like small sacs.
Nucleolus • The nucleolus is within the nucleus. • Recall, the nucleus contains the DNA and is the command center of the cell. • The nucleolus is where ribosomes are made.
Making your own Cell Analogy! • First complete the handout. • Then get into groups of 3. • Obtain a large sheet of paper from Caitlin, Saydie, or me. • Make your own cell analogy representing the organelles. Draw it and color it. • Ex. Shoe factory is the ribosome and shoes are proteins. • Your cell analogy can be anything! Just as long as the cell analogy’s parts represent organelles and their functions.
Animals vs. Plants • Plants have much larger vacuoles • Plants have an extra layer beyond the cell membrane called the cell wall. • Important for structure and rigidity. • Plants do not have lysosomes. • Plants have organelles called chloroplasts. • Responsible for converting light energy from the sun into chemical energy in sugars.
Eukaryotes vs. Prokaryotes • Eukaryotes have eukaryotic cells. • Animal cells and Plant Cells • Prokaryotes have prokaryotic cells. • Bacteria