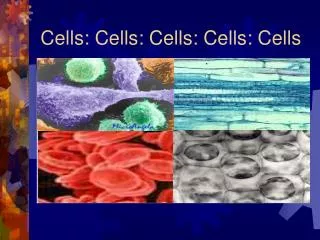
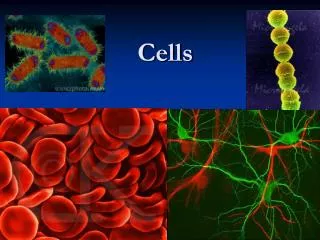
Cells
210 likes | 341 Vues
This overview examines the similarities and differences among various cell types, focusing on eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. It integrates examples from human epidermis, cardiac muscle, plant stems and leaves, and amoeba. Key components of the cell theory are highlighted, emphasizing that all living things are composed of cells and that new cells arise from existing ones. The distinctions between complex eukaryotic cells and simpler prokaryotic cells, including their structures and functions, are discussed for a clearer understanding of cellular biology.

Cells
E N D
Presentation Transcript
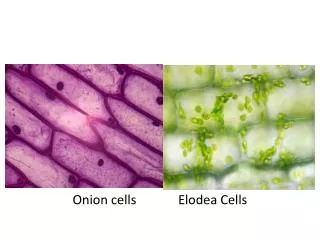
What are some similarities and differences that you observed by looking at a variety of cells?
The Cell Theory • All living things are composed of cells. • Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. • New cells are produced from existing cells.
Types of Cells • Two kinds of cells depending on whether they have a nucleus Eukaryote Prokaryote Genetic material
Prokaryotes • Genetic material (DNA) is notcontained in a nucleus • Usually small and simple
Prokaryotes The ONLY prokaryotes in the world are BACTERIA.
Eukaryotes • Usually larger and more complex than prokaryotes. • May be unicellular like an amoeba or multicellular like a plant
Eukaryotes • Contain dozens of specialized structures called organelles. • Includes protists, fungi, plants and animals.
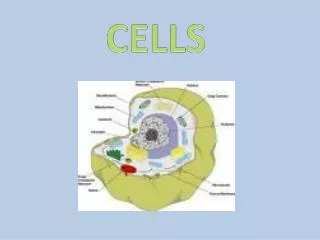
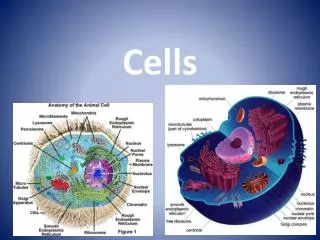
Eukaryotic cell structure • Two major parts: • Nucleus • Cytoplasm-portion of the cell outside the nucleus
You have 3 minutes to compare your notes with a neighbor. Be sure to ask questions and fill in any blanks you may have in your notes at this time.