The Civil War
460 likes | 617 Vues
The Civil War. Chapter 14. Why were plantation owners ready to defend slavery and the southern way of life?. A Divided Nation. The Civil War had a profound impact on daily life in South Carolina Before the Civil War, plantation owners had made a good living on cash crops.

The Civil War
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Civil War Chapter 14
Why were plantation owners ready to defend slavery and the southern way of life?
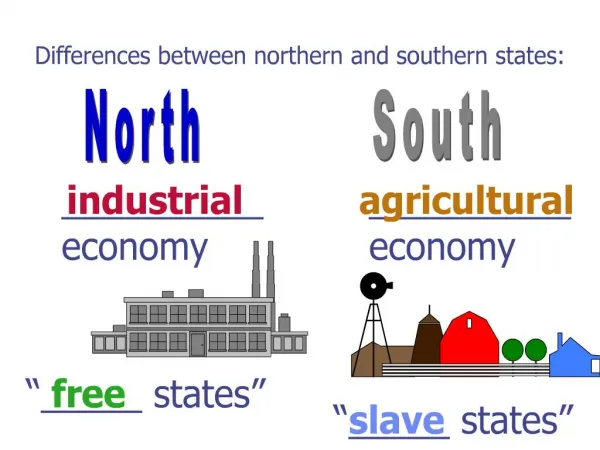
A Divided Nation • The Civil War had a profound impact on daily life in South Carolina • Before the Civil War, plantation owners had made a good living on cash crops. • Slave labor made the plantation owners wealthy and gave them social and political status • Therefore the plantation owners defended slavery and the southern way of life.
A Divided Nation • When Lincoln was elected President • ~Plantation owners were afraid that they were going to lose everything. • ~S C’s legislative meeting voted to break away from the Union and form their own country…
Why did South Carolina decide to break away from the Union and form their own country?
A Divided Nation • The Confederate States of America • Why? To protect slavery and state’s rights • Richmond, Virginia became the Confederate’s capital • Jefferson Davis became the Confederate’s president. • Washington DC & Lincoln The solid color red states were the slave states that seceded and formed the Confederate States of America. The striped states are slave states that remained part of the Union.
A Divided Nation • The North (the Union) • Didn’t see the South as a new nation • Saw the South as being states in rebellion & fought to keep the Union together • The South (the Confederacy) • Saw themselves as independent • Fought to get the invading Northern army off of their land. The solid color red states were the slave states that seceded and formed the Confederate States of America. The striped states are slave states that remained part of the Union.
In what areas was the North better prepared for war? • In what areas was the South better prepared for war?
In what areas was the North better prepared for war? • In what areas was the South better prepared for war?
A Divided Nation • The North was better prepared for war in terms of… • Population., number of states, weapons, money, railroads, factories (to make weapons and supplies), and having a working monetary system in place • The South had… • A strong military tradition & skill • A cause for which they were willing to fight
Battle Strategies • The military strategy of the North was fourfold: • To blockade Southern ports to cut off supplies from Europe • To break the Confederacy in two at the Mississippi River • To destroy communication and transportation systems • To attack the Confederate capital at Richmond, Virginia • This was known as the Anaconda Plan The Anaconda Plan Designed to squeeze the South the way an Anaconda snake squeezes it’s prey.
What was the South’s military strategy? • Why didn’t the Southern military strategy of withholding cotton work?
Battle Strategies • The Southern Strategy • Fight a defensive war, using supplies from Europe gained from the sale of cotton • Until the Northern forces tired of the war • Eventually, the South quit selling cotton to European countries to get them to enter the war • This plan didn’t work because… • European countries started to buy cotton from other countries &… • The South ended up with no supplies & a lot of unusable cotton Cotton was so important to the South that there was no question in their minds’ that cotton was king.
What did the South use to get around the Northern blockade? • What was the northern blockade in doing?
Battle Strategies • The Northern blockade was effective in South Carolina • Despite the efforts of blockade runners and… • The use of a new technology • Such as the submarine the H.L. Hunley • The blockade was devastating to the South because… • It kept the Confederate Army from receiving supplies A map of the Union barricade, and The Hunley
Where were the first shots of the civil war fired? (Be sure to include the location of the fort)
The Civil War Begins • Most of the fighting of the Civil War took place in northern Virginia & along the Mississippi River • There were several battles that took place in South Carolina. • The first shots of the war were fired at Fort Sumter when northern ships attempted to re-supply the federal fort in Charleston Harbor. • This and the Battle of 1st Manassas in Virginia were major victories for the South and made them hopeful of winning the war.
What was the first major setback for the Confederate Army? • How did the continued presence of the Union troops in Port Royal affect South Carolina’s shipping?
The Battle Continues • The 1st major setback for the Confederate Army • Union troops captured the areas surrounding Port Royal Sound along the coast near Hilton Head • These areas remained under Union control throughout the Civil War • The Union prevented ships from importing or exporting from South Carolina ports The Port Royal Sound battle ground across the river from the soldiers.
Port Royal was used as a base to attack which South Carolina city? • Who were the 54th Massachusetts and what did they do?
The Battle Continues • Union forces laid siege to Charleston attacking from Port Royal • Bombarding the city for over a year • During this campaign, the 54th Massachusetts regiment • African American soldiers • along with their Colonel Robert Gould Shaw • Led the charge on Fort Wagner at the mouth of Charleston Harbor The 54th Massachusetts regiment and Colonel Robert Gould Shaw
The Battle Continues • Robert Smalls • A 23 year old harbor pilot • Had knowledge of navigating the harbor • Piloted a Confederate, ship while the white crew was ashore, through the harbor. • Giving the appropriate signals to the confederate forts • Surrendered the ship to the Union at the blockade • Provided the Union with valuable information about the Confederate fortifications
The Battle Continues • Robert Smalls • After the Civil War: • Served as an officer in the State Militia • Served as a state legislator • Helped to draft the Constitution of SC • Served as a 5 term Congressman from SC Congressman Smalls
What two ways were wealthy slave owners involved in the Civil War military service?
The Poor Man’s Fight • Many of the wealthiest slave owners volunteered and served as officers in the Confederate army. • Others were exempt from service under the “20 slave” law • The war became known as “the rich man’s war, the poor man’s fight” when… • Many rich got out of military service, while the poorer could not An unnamed private in the Union Army.
The Poor Man’s War • Most Confederate soldiers • Grew up on farms in the rural areas • Had experience with guns for hunting • They had little formal military training • Many Union soldiers • From cities such as New York, Boston & Philadelphia • Many had worked in factories & manufacturing plants • Some were recent immigrants to the U S New York’s 71st Infantry Regiment
The Poor Man’s Fight • Soldiers on both sides experienced the devastation of war. • Disease spread rapidly through military camps because … • Unsanitary practices and close quarters. • Soldiers on both sides were tired, sick, hungry, wet, scared, and lonely. • No matter which side, the soldiers fought bravely to defend their cause.
When the men left for war, what did women do? • Why were women’s lives difficult during the war?
Civil War Living • Women • Were left behind to tend to the farms and run the plantations. • The lives of women were made especially difficult because of shortages of supplies such as clothes and food needed by the southern soldiers. Clothing was often patched to make it last so that soldiers could have the use of new clothes
Why did women need to find substitutes for products or go without products? • What did women do to help the war’s cause? • As Union forces advanced, what did women do?
Civil War Living • Women found substitutes for many products or did without • Inflation made Confederate money worthless. • Some women served as nurses to the wounded or raised money for the cause. • Many were forced to flee their homes as Union forces advanced, only to return to ruins.
What did both slave and free children do during the war? • What roles did children have in the armed forces?
Civil War Living • Civil War also had an impact on children • Both slave and free children assisted around the farm or plantation. • They suffered the same hardships and shortages as everyone else during the war. • Some boys as young as 10 enlisted in the armed forces, served as drummer boys and standard (flag) bearers, were sometimes caught in the crossfire and died for their cause Johnny Shiloh was only 10 years-old when he joined the Union army.
What two ways did slaves receive their freedom during the war? • What did the Emancipation Proclamation say? • What was the effect of the Emancipation Proclamation in the Confederate states?
Civil War Living • Slaves & the War • Fled to nearby Union lines to claim their freedom • Stayed on the plantation and waited for the Union army to free them. • Emancipation Proclamation President Lincoln • All slaves in areas that had not yet been captured by the Union army were free. • These states, still under the control of the Confederacy, did not obey the Union president. Henry Louis Stephens’ painting of a man reading a newspaper entitled “Presidential Proclamation/Slavery”
When African Americans joined the Union Army, how were they treated?
Civil War Living • Unoccupied Confederate states ignored Lincoln • The Emancipation Proclamation never actually freed a single slave. • It did allow African Americans to fight for the Union Army and many volunteered immediately. • Although African American troops served as well as any other soldier, they were often discriminated against.
When General William Sherman marched to the sea, what was his goal? • How did Sherman’s march affect South Carolina?
Sherman’s March to the Sea • Union General William Sherman marched into South Carolina after his capture of Atlanta and his march-to-the-sea. • Sherman’s goal was to make “total war”, bringing the war home to civilians to convince the South to surrender. • This had a direct impact on the civilians in SC • Destroying homes, plantations, railroads and towns along the way. Map of the route taken by Sherman & his troops
What happened to Columbia when Sherman’s troops reached it? • Why did Sherman want to convince South Carolina to surrender?
Sherman’s March to the Sea • The state house in Columbia was under construction as Sherman marched through state’s capital. • The capital building was shelled by Sherman’s troops and the city was set on fire Even though there is some controversy over who started the fire • Sherman especially wanted to convince SC to surrender since it was the first state to secede from the Union. “Sherman's March of 1865 burned the majority of downtown Columbia to the ground. This is a view down Main Street, taken from the capitol.” -Sciway.net
When the war was over, what happened to South Carolina’s plantation owners?
The Aftermath • When the Civil War ended, many plantations had been destroyed. • War brought an end to slavery and the plantation owners lost the fortunes that had been tied up in slave property. • The difficult period of rebuilding had just begun for South Carolina and other Southern states.