The Great War
690 likes | 794 Vues
Explore how Queen Victoria's descendants ruled Europe, leading to WWI. Learn about alliances, nationalism, and the assassination that ignited the war.

The Great War
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Great War Chapter 20
Kaiser Wilhelm of Germany was her grandson. Her descendants ruled Europe
King George V of England was her grandson. Her descendants ruled Europe
Czar Nicholas of Russia was her grandson-in-law (married to her granddaughter Alexandra) Her descendants ruled Europe
Another granddaughter became Queen of Romania. • A great-granddaughter became Queen of Yugoslavia. • Another great-granddaughter became Queen of Greece.
Her great-great grandson is the present day King of Spain. • Her great granddaughter is the present day Queen of England.
People believed that the world was getting better through science and the power of mankind. • Rise of industrialism • Higher standard of living • Diseases eradicated • Efforts at international peace & cooperation The “Progressive Era”
Some International Peace Efforts • Red Cross • International Telegraph Union • Universal Postal Union • Standard system of weights & measures • Pan American Union • Revival of the Olympic Games 1896 • Nobel Peace Prize • Carnegie’s Peace Palace @ The Hague
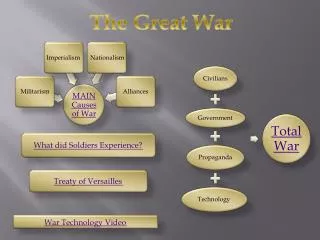
Extreme Nationalism – others inferior • Militarism – glorified war, national glory • Imperialism – competition for colonies • Rival Alliances – defense pacts Reasons to Fear War (James 4:1)
Bismarck – helped to unify Germany (1870). • Keep France from rising after defeat in Franco-Prussian War • Several alliances formed and reshaped between 1873 and 1877. • Germany & Austria-Hungary Steps Toward War
Kaiser Wilhelm II of Germany – proud, arrogant • Forced Bismarck to resign as chancellor • Heightened Europe’s tensions Steps Toward War
Kaiser Wilhelm’s mistakes: • 1. Allowed the reinsurance Treaty with Russia to expire, leading to an alliance between Russia and France. • 2. Antagonize Britain by threatening her naval domination, interfering with her colonies in Africa. • This antagonism led to a British-French alliance called the Entente Cordiale. • The Russia joined them to form the Triple Entente (Britain, France, Russia) Steps Toward War
German attempts to control Morocco • Balkans independent of Turkey but fought each other • Austria-Hungary didn’t like the instability on her border and actually wanted possession of the Balkans. • Russia intervened to protect their “slavic” brothers the Balkans. The Powder Keg of Europe
The Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand and Duchess Sophie of Austria by a Serbian nationalist on June 28, 1914 was the spark that started The Great War. The Catalyst: Assassination
10,000,000 killed. • 6,000,000 crippled for life. • …and the bitterness that led to yet another conflict. The Result
Central Powers • Germany • Austria
Allies • France • Britain • Russia
Austria blamed the Serbian government for the assassination. • Ultimatum: Austria demanded that Serbia submit to its rule. • Serbia agreed, but Austria declared war on Serbia on July 28, 1914. The Web of War
Russia mobilized its military (July 30) to keep Austria from taking over the Balkan states. • The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains, which run through the center of Bulgaria into eastern Serbia. The Web of War
Austria’s ally GERMANY declared war on Russia. August 1, 1914 The Tangled Web
Russia and France had a mutual security pact, promising to protect one another if attacked. • Germany demanded to know France’s intentions in the matter since France’s ally was at war with Germany. • The French mobilized their troops because they were afraid of the German military buildup. (They share a border.) The Tangled Web
Germany felt France’s move was one of aggression and declared war on FRANCE. August 3, 1914 The Tangled Web
BRITAIN had signed a treaty promising to protect BELGIUM’S neutrality. • Germany pushed its way through Belgium to attack France. August 5, 1914 • Britain intervened to help the Belgians and entered the war. The Tangled Web
1. Serbian guy kills Archduke of Austria. 7/23 • 2. Austria decl. war on Serbia. 7/28 • 3. Russia mobilizes troops. 7/30 • 4. Germany decl. war on Russia. 8/1 • 5. Russian-French security pact. • 6. France mobilizes troops. • 7. Germany decl. war on France. 8/3 • 8. Britain treaty to defend Belgium. • 9. Germans enters Belgium to attack France. 8/5 • 10. Britain enters war to help Belgium. Sequence of Events
Why was Austria’s declaration of war on Serbia a turning point in history? • What other options were available to Austria?
War in the West – • Germans attack France through neutral Belgium. • The troops build trenches and neither side gains or loses much ground. (maps page 525) • Schlieffen Plan – Germany would try to avoid a two-front war by attacking France by marching through neutral Belgium. A Two-Front War
War in the East – • Germans v. Russians. Russians not industrialized and can’t supply troops. • Ottoman warzone. British enter to hold straits. • Bulgarians and Turks fight with Germans. A Two-Front War
Western Front – • A stalemate in trench warfare. • War of attrition. The Course of the War
Italy started neutral, then joined the Allies, mostly in order to gain more territory. The Course of the War
Machine guns • Flame throwers • Poisonous gas-filled artillery shells • Gas masks and gas detection devices • “Big Bertha” guns – range 80 miles • Tanks • Airplanes • Zeppelins • U-Boats New Weapons of War
The British blockade Germany to prevent war goods from getting to Germany. War at Sea
In response to the British blockade, Germany deploys its u-boats. (unterseeboot)
No ships can enter the “war zone” around Britain without threat of being sunk.
Typically, before a warship would attack, it would give a warning to the passengers to abandon ship. • A submarine would lose its element of surprise and become vulnerable to attack itself, so submarines wouldn’t give warnings.
Germany had taken out ads in the New York Times warning Americans NOT to travel on British ships or in the waters around Britain.
A German u-boat sunk a passenger liner. • 1,198 passengers and crew perished as the Lusitania went down, including 128 Americans on May 1, 1915. • The sinking caused the Germans to lose support in the United States.
Germany said that they had attacked the Lusitania in self-defense because it was carrying munitions to the Allies to be used against Germany.
The cargo manifest shows that the Lusitania was carrying ammunition, powder, shrapnel, rifles, etc.
Under pressure of the British blockade, Germany declared unrestricted submarine warfare: they would attack ANY vessel in the war zone without warning. • Wilson broke off diplomatic relations with Germany on Feb. 3, 1917. U.S. Involvement
British intelligence agents intercepted a telegraph from German Foreign Minister Arthur Zimmerman to the Mexican government to enlist their aid in Germany’s war effort. Zimmerman promised Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona to Mexico if it agreed to join the Central Powers. The U.S. was outraged. (March 1, 1917) The Zimmerman Telegraph
The Germans sink 4 unarmed American merchant vessels. (mid-March) • Wilson asked Congress to declare war on Germany. They did so and Wilson signed it on April 6, 1917. U.S. Enters the War
Propaganda In World War I